Management of adverse events in patients with acute myeloid leukemia in remission receiving oral azacitidine: experience from the phase 3 randomized QUAZAR AML-001 trial
- PMID: 34454540
- PMCID: PMC8401338
- DOI: 10.1186/s13045-021-01142-x
Management of adverse events in patients with acute myeloid leukemia in remission receiving oral azacitidine: experience from the phase 3 randomized QUAZAR AML-001 trial
Abstract
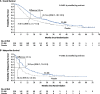
Background: Most older patients with acute myeloid leukemia (AML) who attain morphologic remission with intensive chemotherapy (IC) will eventually relapse and post-relapse prognosis is dismal. In the pivotal QUAZAR AML-001 trial, oral azacitidine maintenance therapy significantly prolonged overall survival by 9.9 months (P < 0.001) and relapse-free survival by 5.3 months (P < 0.001) compared with placebo in patients with AML in first remission after IC who were not candidates for transplant. Currently, the QUAZAR AML-001 trial provides the most comprehensive safety information associated with oral azacitidine maintenance therapy. Reviewed here are common adverse events (AEs) during oral azacitidine treatment in QUAZAR AML-001, and practical recommendations for AE management based on guidance from international cancer consortiums, regulatory authorities, and the authors' clinical experience treating patients in the trial.
Methods: QUAZAR AML-001 is an international, placebo-controlled randomized phase 3 study. Patients aged ≥ 55 years with AML and intermediate- or poor-risk cytogenetics at diagnosis, who had attained first complete remission (CR) or CR with incomplete blood count recovery (CRi) within 4 months before study entry, were randomized 1:1 to receive oral azacitidine 300 mg or placebo once-daily for 14 days in repeated 28-day cycles. Safety was assessed in all patients who received ≥ 1 dose of study drug.
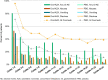
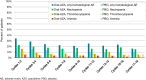
Results: A total of 469 patients received oral azacitidine (n = 236) or placebo (n = 233). Median age was 68 years. Patients received a median of 12 (range 1-80) oral azacitidine treatment cycles or 6 (1-73) placebo cycles. Gastrointestinal AEs were common and typically low-grade. The most frequent grade 3-4 AEs during oral azacitidine therapy were hematologic events. AEs infrequently required permanent discontinuation of oral azacitidine (13%), suggesting they were effectively managed with use of concomitant medications and oral azacitidine dosing modifications.
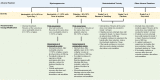
Conclusion: Oral azacitidine maintenance had a generally favorable safety profile. Prophylaxis with antiemetic agents, and blood count monitoring every other week, are recommended for at least the first 2 oral azacitidine treatment cycles, and as needed thereafter. Awareness of the type, onset, and duration of common AEs, and implementation of effective AE management, may maximize treatment adherence and optimize the survival benefits of oral azacitidine AML remission maintenance therapy. Trial registration This trial is registered on clinicaltrials.gov: NCT01757535 as of December 2012.
Keywords: CC-486; Maintenance; Oral azacitidine; Safety.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
F.R. reports honoraria and consulting fees from Bristol Myers Squibb and Celgene; and Research funding from Bristol Myers Squibb. G.J.R. reports Consultancy or Advisory Board or Data and Safety Monitoring Committee: AbbVie, Actinium, Agios, Amphivena, Amgen, Argenx, Array Biopharma, Astex, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Bayer, Bristol Myers Squibb, Celgene, Celltrion, Daiichi Sankyo, Eisai, Epizyme, GlaxoSmithKline, Helsinn, Janssen, Jasper Therapeutics, Jazz, Mesoblast, MEI Pharma (IDMC Chair), Novartis, Orsenix, Otsuka, Pfizer, Roche/Genentech, Sandoz, Takeda (IRC Chair), Trovagene; Research Support: Cellectis. A.H.W. reports study-related fees and personal fees from Celgene; royalties from Walter and Eliza Hall Institute of Medical Research; grants from the Medical Research Future Fund; grants and personal fees from Servier, AbbVie, Novartis, Celgene, Astra Zeneca, and Janssen; and personal fees from Astellas, Pfizer, Macrogenics, and Amgen. H. Döhner reports personal fees from Abbvie, Agios, Astellas, Astex Pharmaceuticals, Helsinn, Janssen, Oxford Biomedicals, and Roche; grants and personal fees from Amgen, Celgene, Jazz Pharmaceuticals, and Novartis; and grants from AROG Pharmaceuticals, Bristol Myers Squibb, Pfizer, and Sunesis. D.S. reports honoraria from Novartis, Celgene, Amgen, Janssen-Cilag, AbbVie, Alexion, GSK, MSD, Pfizer, Sanofi, Takeda, Incyte, and Teva; consultancy for Novartis, Celgene, Amgen, Janssen-Cilag, AbbVie, Alexion, GSK, MSD, Pfizer, Sanofi, Takeda, Incyte, and Teva; and speakers’ bureau participation for Novartis, Celgene, Amgen, MSD, Takeda, and Teva. P.M. reports Research support and advisory board by Celgene-BMS. H.Sayar reports advisory board participation for BMS. H.Safah reports speaker’s bureau participation for Incyte, Celgene/BMS, Sanofi, Karyopharm, and Amgen. D.H. reports research support from Celgene/BMS. H. Dombret reports Research support and advisory board participation for Celgene-BMS. B.S., R.B., J.Z., and C.L.B. are employed at and have equity ownership in Bristol Myers Squibb. I.L.T. was formerly employed at Celgene, a Bristol-Myers Squibb Company, and had equity ownership in Bristol Myers Squibb. C.P., M.M., A.F.-A., W.T., S.K.S., and T.C. report no conflicts.
Figures
References
-
- National Cancer Institute (NCI). Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program. Cancer Stat Facts: Leukemia—Acute Myeloid Leukemia (AML). https://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/amyl.html. Accessed 1 March 2021.
-
- Cheson BD, Bennett JM, Kopecky KJ, Buchner T, Willman CL, Estey EH, et al. Revised recommendations of the International Working Group for diagnosis, standardization of response criteria, treatment outcomes, and reporting standards for therapeutic trials in acute myeloid leukemia. J Clin Oncolo. 2003;21(24):4642–4649. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2003.04.036. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

