The impact of the COVID-19 epidemic on primary care in South-eastern France: implementation of a real-time monitoring system based on regional health insurance system data
- PMID: 34454792
- PMCID: PMC8818324
- DOI: 10.1016/j.respe.2021.07.006
The impact of the COVID-19 epidemic on primary care in South-eastern France: implementation of a real-time monitoring system based on regional health insurance system data
Abstract
Background: The spring 2020 COVID-19 epidemic severely impacted France's healthcare system. The associated lockdown (17 March- 11 May 2020) and the risk of exposure to SARS-CoV-2 led patients to change their use of healthcare. This article presents the development and implementation of a real-time system to monitor i) private doctors' activity in South-eastern France, and ii) changes in prescription of drugs for people with diabetes, mental health disorders and for certain vaccines from Mars 2020 to October 2020.
Methods: Data extracted from the regional healthcare insurance databases for 2019 and 2020 were used to construct indicators of healthcare use. They were calculated on a weekly basis, starting from week 2 2020 and compared for the same period between 2019 and 2020.
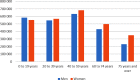
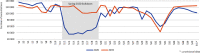
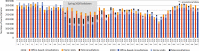
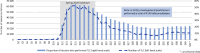
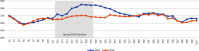
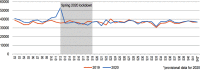
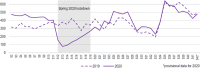
Results: Private doctors' activity decreased during the spring 2020 lockdown (by 23 % for general practitioners and 46 % for specialists), followed by an almost complete return to normal after it ended until week 41. Over the same period, a huge increase in teleconsultations was observed, accounting for 30 % of private doctors' consultations at the height of the crisis. The start of the lockdown was marked by a peak in drug prescriptions, while vaccinations declined sharply (by 39 % for the measles, mumps and rubella (MMR) vaccine in children under 5 years old, and by 54 % for human papillomavirus vaccine in girls aged 10-14 years old).
Conclusion: The ongoing COVID-19 epidemic may lead to health consequences other than those directly attributable to the disease itself. Specifically, lockdowns and foregoing healthcare could be very harmful at the individual and population levels. The latter issue is a concern for French public authorities, which have implemented actions aimed at encouraging patients to immediately seek treatment. However, the COVID-19 crisis has also created opportunities, such as the roll-out of teleconsultation and tele-expertise. The indicators described here as part of the monitoring system can help public decision-makers to become more responsive and to implement tailored actions to better meet the general population's healthcare needs.
Position du problème: L’épidémie de Covid-19 du printemps 2020 a fortement affecté le système de soins. Le confinement et les risques d'exposition au coronavirus ont incité les patients à modifier leur recours aux soins. L'objectif était de partager un retour d'expérience sur la mise en place d'un dispositif de surveillance en temps réel de l'activité des médecins libéraux de la région Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur, et de l’évolution des remboursements de médicaments prescrits aux assurés du régime général pour le diabète, pour des troubles de la santé mentale et pour certains vaccins.
Méthodes: Les données ont été extraites à partir des bases régionales de l'Assurance maladie pour les années 2019 et 2020. Elles ont permis de construire des indicateurs en date de soins pour le régime général stricto sensu, calculés de façon hebdomadaire, à partir de la semaine 2.
Résultats: On constate une chute d'activité des médecins libéraux lors du confinement (-23 % pour les médecins généralistes ; -46 % pour les spécialistes), suivie d'un quasi retour à la normale par la suite. Dans le même temps, les téléconsultations ont connu un véritable essor : elles ont constitué 30 % des actes des médecins libéraux au plus fort de la crise. Le début du confinement a été marqué par un pic d'approvisionnement en médicaments, tandis que la vaccination a fortement diminué (-39 % concernant le vaccin contre la rougeole, les oreillons et la rubéole chez les enfants de moins de 5 ans ; -54 % pour le vaccin contre les papillomavirus humains chez les filles de 10-14 ans).
Conclusion: L’épidémie de Covid-19 risque d'entraîner d'autres conséquences sanitaires que celles directement imputables à la Covid-19 elle-même. Le renoncement aux soins pourrait causer des retards de soins fortement préjudiciables aux individus et à la collectivité. Ces questions inquiètent les autorités publiques, qui mettent en place des actions visant à inciter les patients à se soigner sans tarder. Mais la crise liée à la Covid-19 a aussi créé des opportunités, telles que le déploiement de la téléconsultation et de la téléexpertise. Bien que partiels, les indicateurs mis en œuvre peuvent permettre aux décideurs publics d’être réactifs et de mettre en place certaines actions afin de répondre aux besoins de santé des populations.
Keywords: COVID-19; Covid-19; Doctors; Drugs; Healthcare use; Médecins; Médicaments; Private healthcare; Public health; Recours aux soins; Santé publique; Soins de ville; Vaccination.
Copyright © 2021 Elsevier Masson SAS. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Monziols M, Chaput H, Verger P, Scronias D, Ventelou B, et al. Comment les médecins généralistes ont-ils exercé leur activité pendant le confinement lié au Covid-19 ? Drees Études & Résultats. 2020:1150.
-
- Assurance Maladie. Communiqué des dépenses. Les remboursements de soins du Régime Général à fin mai 2020.
-
- Andolfatto D, Labbé D. Covid-19 : Une défaite française. Rev Politique et Parlementaire. 2020 halshs-02882877.
-
- Ministère des solidarités et de la santé . 2020. Prise en charge hors Covid-19.
-
- Santé Publique France . 2020. Covid-19 et continuité des soins. Continuer de se soigner, un impératif de santé publique.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

