Arhgap22 Disruption Leads to RAC1 Hyperactivity Affecting Hippocampal Glutamatergic Synapses and Cognition in Mice
- PMID: 34455539
- PMCID: PMC8639580
- DOI: 10.1007/s12035-021-02502-x
Arhgap22 Disruption Leads to RAC1 Hyperactivity Affecting Hippocampal Glutamatergic Synapses and Cognition in Mice
Abstract
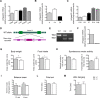
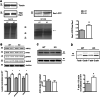
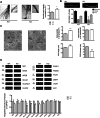
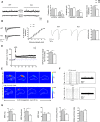
Rho GTPases are a class of G-proteins involved in several aspects of cellular biology, including the regulation of actin cytoskeleton. The most studied members of this family are RHOA and RAC1 that act in concert to regulate actin dynamics. Recently, Rho GTPases gained much attention as synaptic regulators in the mammalian central nervous system (CNS). In this context, ARHGAP22 protein has been previously shown to specifically inhibit RAC1 activity thus standing as critical cytoskeleton regulator in cancer cell models; however, whether this function is maintained in neurons in the CNS is unknown. Here, we generated a knockout animal model for arhgap22 and provided evidence of its role in the hippocampus. Specifically, we found that ARHGAP22 absence leads to RAC1 hyperactivity and to an increase in dendritic spine density with defects in synaptic structure, molecular composition, and plasticity. Furthermore, arhgap22 silencing causes impairment in cognition and a reduction in anxiety-like behavior in mice. We also found that inhibiting RAC1 restored synaptic plasticity in ARHGAP22 KO mice. All together, these results shed light on the specific role of ARHGAP22 in hippocampal excitatory synapse formation and function as well as in learning and memory behaviors.
Keywords: ARHGAP22; Dendritic spines; Hippocampus; Learning and memory; Synaptic plasticity.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Rho-GTPase-activating protein interacting with Cdc-42-interacting protein 4 homolog 2 (Rich2): a new Ras-related C3 botulinum toxin substrate 1 (Rac1) GTPase-activating protein that controls dendritic spine morphogenesis.J Biol Chem. 2014 Jan 31;289(5):2600-9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.534636. Epub 2013 Dec 18. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24352656 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of synaptic Rac1 activity, long-term potentiation maintenance, and learning and memory by BCR and ABR Rac GTPase-activating proteins.J Neurosci. 2010 Oct 20;30(42):14134-44. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1711-10.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20962234 Free PMC article.
-
Disruption of ArhGAP15 results in hyperactive Rac1, affects the architecture and function of hippocampal inhibitory neurons and causes cognitive deficits.Sci Rep. 2016 Oct 7;6:34877. doi: 10.1038/srep34877. Sci Rep. 2016. PMID: 27713499 Free PMC article.
-
The cellular function of srGAP3 and its role in neuronal morphogenesis.Mech Dev. 2013 Jun-Aug;130(6-8):391-5. doi: 10.1016/j.mod.2012.10.005. Epub 2012 Nov 2. Mech Dev. 2013. PMID: 23127797 Review.
-
FilGAP and its close relatives: a mediator of Rho-Rac antagonism that regulates cell morphology and migration.Biochem J. 2013 Jul 1;453(1):17-25. doi: 10.1042/BJ20130290. Biochem J. 2013. PMID: 23763313 Review.
Cited by
-
Interaction models matter: an efficient, flexible computational framework for model-specific investigation of epistasis.BioData Min. 2024 Feb 28;17(1):7. doi: 10.1186/s13040-024-00358-0. BioData Min. 2024. PMID: 38419006 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal network activity and connectivity are impaired in a conditional knockout mouse model with PCDH19 mosaic expression.Mol Psychiatry. 2024 Jun;29(6):1710-1725. doi: 10.1038/s41380-023-02022-1. Epub 2023 Mar 30. Mol Psychiatry. 2024. PMID: 36997609 Free PMC article.
-
Genomic insights into adaptation and inbreeding among Sub-Saharan African cattle from pastoral and agropastoral systems.Front Genet. 2024 Jul 25;15:1430291. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2024.1430291. eCollection 2024. Front Genet. 2024. PMID: 39119582 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

