First-in-Human Study of Bamlanivimab in a Randomized Trial of Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19
- PMID: 34455583
- PMCID: PMC8653186
- DOI: 10.1002/cpt.2405
First-in-Human Study of Bamlanivimab in a Randomized Trial of Hospitalized Patients With COVID-19
Abstract
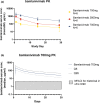
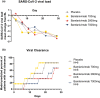
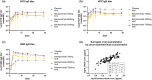
Therapeutics for patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) are urgently needed during the pandemic. Bamlanivimab is a potent neutralizing monoclonal antibody that blocks severe acute respiratory syndrome-coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) attachment and entry into human cells, which could potentially lead to therapeutic benefit. J2W-MC-PYAA was a randomized, double-blind, sponsor unblinded, placebo-controlled, single ascending dose first-in-human trial (NCT04411628) in hospitalized patients with COVID-19. A total of 24 patients received either placebo or a single dose of bamlanivimab (700 mg, 2,800 mg, or 7,000 mg). The primary objective was assessment of safety and tolerability, including adverse events and serious adverse events, with secondary objectives of pharmacokinetic (PK) and pharmacodynamic analyses. Treatment-emergent adverse event (TEAE) rates were identical in the placebo and pooled bamlanivimab groups (66.7%). There were no apparent dose-related increases in the number or severity of TEAEs. There were no serious adverse events or deaths during the study, and no discontinuations due to adverse events. PKs of bamlanivimab is linear and exposure increased proportionally with dose following single i.v. administration. The half-life was ~ 17 days. These results demonstrate the favorable safety profile of bamlanivimab, and provided the initial critical evaluation of safety, tolerability, and PKs in support of the development of bamlanivimab in several ongoing clinical trials.
© 2021 Eli Lilly and Company. Clinical Pharmacology & Therapeutics published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
P.C. reports grants from Eli Lilly and Company, Gilead, and the National Institutes of Health (NIH), and scientific advisory board member for Eli Lilly and Company, Gilead, Rigel Pharmaceuticals, and Humanigen. N.R. reports grants from Eli Lilly and Company, Merck, Pfizer, Quidel, and Sanofi‐Pasteur. M.J.M. has received research grants from Eli Lilly and Company, Pfizer, and Sanofi, and serves on advisory boards for Pfizer and Meissa Vaccines. W.F. reports research funding provided to UNC from Ridgeback Biopharmaceuticals, Eli Lilly and Company, and Regeneron, consultancy fees from Merck and Roche and served on adjudication committee for Janssen and Syneos. M.D. reports personal fees from Genentech‐Roche, Partner Therapeutics, Tillots Pharma, ORIC Pharmaceuticals, Moderna, AzurRx, SQZ, and WebMD, grants from Novartis and Eli Lilly and Company, and is a scientific advisory board member for Neoleukin Therapeutics. A.S. is an advisory board member for Eli Lilly and Company. G.D., Y.G.L., J.C., K.P., E.C., P.B.A., J.P., J.F., R.J.B., P.K., A.N., and C.B. are employees and shareholders of Eli Lilly and Company. All other authors declared no competing interests for this work.
Figures

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

