Green extraction of proteins, umami and other free amino acids from brown macroalgae Ascophyllum nodosum and Fucus vesiculosus
- PMID: 34456508
- PMCID: PMC8383259
- DOI: 10.1007/s10811-021-02569-y
Green extraction of proteins, umami and other free amino acids from brown macroalgae Ascophyllum nodosum and Fucus vesiculosus
Abstract
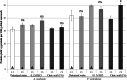
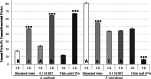
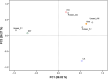
Seaweeds are a valuable potential source of protein, as well as free amino acids (FAAs) with umami flavour which are in high demand by the food industry. The most commonly used flavouring agents in the food industry are chemically synthesised and therefore are subject to concerns regarding their safety and associated consumer resistance. This study focuses on the effects of extraction time (1 and 2 h) and solvents (0.1 M HCl, 1% citric acid and deionised water) on the extraction of protein and FAAs including umami FAAs from Irish brown seaweeds (Ascophyllum nodosum and Fucus vesiculosus). Extraction yields were influenced by both the extraction solvent and time, and also varied according to the seaweed used. Both seaweeds investigated were found to be good sources of protein, FAAs including umami FAAs, demonstrating potential application as flavouring agents in the food industry. Overall, the use of green solvents (deionised water and citric acid) resulted in higher recoveries of compounds compared to HCl. The results of this study will facilitate the use of more sustainable solvents in industry for the extraction of proteins and flavouring agents from seaweed.
Keywords: Algae; Flavour industry; Flavouring agents; Free amino acids; Green solvents; Phaeophyta; Umami.
© The Author(s) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sequential extraction of fucoidan, laminarin, mannitol, alginate and protein from brown macroalgae Ascophyllum nodosum and Fucus vesiculosus.Int J Biol Macromol. 2024 Jan;256(Pt 1):128195. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2023.128195. Epub 2023 Nov 24. Int J Biol Macromol. 2024. PMID: 38008143
-
Clinical Efficacy of Brown Seaweeds Ascophyllum nodosum and Fucus vesiculosus in the Prevention or Delay Progression of the Metabolic Syndrome: A Review of Clinical Trials.Molecules. 2021 Jan 30;26(3):714. doi: 10.3390/molecules26030714. Molecules. 2021. PMID: 33573121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Proximate Composition and Nutritional Value of Three Macroalgae: Ascophyllum nodosum, Fucus vesiculosus and Bifurcaria bifurcata.Mar Drugs. 2017 Nov 15;15(11):360. doi: 10.3390/md15110360. Mar Drugs. 2017. PMID: 29140261 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasound, microwave and enzyme-assisted multiproduct biorefinery of Ascophyllum nodosum.Food Chem. 2024 Feb 1;433:137259. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2023.137259. Epub 2023 Aug 25. Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 37672947
-
Source, Extraction, Characterization, and Applications of Novel Antioxidants from Seaweed.Annu Rev Food Sci Technol. 2019 Mar 25;10:541-568. doi: 10.1146/annurev-food-032818-121401. Epub 2019 Jan 23. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol. 2019. PMID: 30673506 Review.
Cited by
-
Biochemical and Nutritional Characterization of Edible Seaweeds from the Peruvian Coast.Plants (Basel). 2023 Apr 27;12(9):1795. doi: 10.3390/plants12091795. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37176854 Free PMC article.
-
Ultrasonic-Assisted Extraction and Antioxidant Potential of Valuable Protein from Ulva rigida Macroalgae.Life (Basel). 2022 Dec 28;13(1):86. doi: 10.3390/life13010086. Life (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36676035 Free PMC article.
-
Extraction of degraded proteins from red and green macroalgae using ultrasonic-assisted extraction and Fenton's reagent in combination.Curr Res Food Sci. 2025 May 27;10:101085. doi: 10.1016/j.crfs.2025.101085. eCollection 2025. Curr Res Food Sci. 2025. PMID: 40529649 Free PMC article.
-
Ascophyllum nodosum (Linnaeus) Le Jolis from Arctic: Its Biochemical Composition, Antiradical Potential, and Human Health Risk.Mar Drugs. 2024 Jan 19;22(1):48. doi: 10.3390/md22010048. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 38276650 Free PMC article.
-
Seaweeds in Food: Current Trends.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jun 12;12(12):2287. doi: 10.3390/plants12122287. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37375912 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Anastas PT, Warner JC. Green chemistry theory and practice. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2000.
-
- Barrena R, Sánchez M. Neophobia, personal consumer values and novel food acceptance. Food Qual Prefer. 2013;27:72–84. doi: 10.1016/j.foodqual.2012.06.007. - DOI
-
- Biancarosa I, Espe M, Bruckner C, Heesch S, Liland N, Waagbø R, Torstensen B, Lock E. Amino acid composition, protein content, and nitrogen-to-protein conversion factors of 21 seaweed species from Norwegian waters. J Appl Phycol. 2017;29:1001–1009. doi: 10.1007/s10811-016-0984-3. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
