Ultrasound-Guided Thoracic Paravertebral Block Enhances the Quality of Recovery After Modified Radical Mastectomy: A Randomized Controlled Trial
- PMID: 34456586
- PMCID: PMC8385420
- DOI: 10.2147/JPR.S325627
Ultrasound-Guided Thoracic Paravertebral Block Enhances the Quality of Recovery After Modified Radical Mastectomy: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
Purpose: Ultrasound-guided thoracic paravertebral block (TPVB) has become increasingly popular for postoperative analgesia after breast surgery. We designed this prospective, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to test the hypothesis that TPVB is superior to placebo in improving the patient quality of recovery following modified radical mastectomy.
Patients and methods: Sixty-eight female patients undergoing elective unilateral modified radical mastectomy were enrolled. Patients were randomized to receive preoperative ultrasound-guided TPVB with 0.5% ropivacaine (TPVB group, n=34) or 0.9% saline (Control group, n=34). The primary outcome was quality of recovery, measured 24 h after surgery using the 40-item Quality of recovery questionnaire (QoR-40). Secondary outcomes were the area under the curve of the visual analog scale pain scores over 24 h, postoperative 24-h morphine consumption, time to first rescue analgesia, length of post-anesthesia care unit stay, postoperative nausea and vomiting, and patient satisfaction.
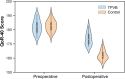
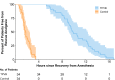
Results: The global QoR-40 score 24 h postoperatively (median [interquartile range]) was 173 [170-177] in the TPVB group and 161 [160-164] in the control group (P<0.001), respectively, with a median difference (95% confidence interval) of 11 (9-14). Compared with the control group, preoperative TPVB decreased the area under the curve of the visual analog scale pain scores over 24 h, reduced postoperative 24-h morphine consumption, prolonged the time to first rescue analgesia, shortened the length of post-anesthesia care unit stay, lessened postoperative nausea and vomiting, and improved the patient satisfaction.
Conclusion: A single preoperative injection of TPVB with ropivacaine enhances the quality of recovery and postoperative analgesia in patients following modified radical mastectomy.
Keywords: breast cancer surgery; pain management; quality of recovery; regional anesthesia; thoracic paravertebral block; ultrasonography.
© 2021 Rao et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflicts of interest in this work.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Ultrasound-guided transversus thoracic muscle plane-pectoral nerve block for postoperative analgesia after modified radical mastectomy: a comparison with the thoracic paravertebral nerve block.Perioper Med (Lond). 2022 Jul 27;11(1):39. doi: 10.1186/s13741-022-00270-3. Perioper Med (Lond). 2022. PMID: 35883207 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Ultrasound-Guided Deep Serratus Anterior Plane Block Combined With Dexmedetomidine as an Adjuvant to Ropivacaine Inpatient Quality of Recovery Scores Undergoing Modified Radical Mastectomy: A Randomized Controlled Trial.Front Oncol. 2022 Mar 31;12:858030. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2022.858030. eCollection 2022. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35433468 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of Ultrasound-Guided Thoracic Paravertebral Block on Postoperative Quality of Recovery in Patients Undergoing Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy: A Randomized Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Trial.J Pain Res. 2023 Apr 19;16:1301-1310. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S405657. eCollection 2023. J Pain Res. 2023. PMID: 37155532 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Efficacy of pectoral nerve block versus thoracic paravertebral block for postoperative analgesia after radical mastectomy: a randomized controlled trial.Br J Anaesth. 2016 Sep;117(3):382-6. doi: 10.1093/bja/aew223. Br J Anaesth. 2016. PMID: 27543533 Clinical Trial.
-
Anesthesia and analgesia in breast surgery: the benefits of peripheral nerve block.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017 Mar;21(6):1341-1345. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28387892 Review.
Cited by
-
A Comparison of the Effectiveness of the Serratus Anterior Plane Block and Erector Spinae Plane Block to that of the Paravertebral Block in the Surgical Treatment of Breast Cancer-A Randomized, Prospective, Single-Blinded Study.J Clin Med. 2024 Aug 16;13(16):4836. doi: 10.3390/jcm13164836. J Clin Med. 2024. PMID: 39200978 Free PMC article.
-
Association of peripheral nerve blocks with patient-reported quality of recovery in female patients receiving breast cancer surgery: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled studies.Can J Anaesth. 2022 Oct;69(10):1288-1299. doi: 10.1007/s12630-022-02295-0. Epub 2022 Jul 26. Can J Anaesth. 2022. PMID: 35882724 English.
-
Assessing Postoperative Benefits of a Nerve Block: Study Design is Critical [Letter].J Pain Res. 2022 Jan 7;15:39-40. doi: 10.2147/JPR.S352469. eCollection 2022. J Pain Res. 2022. PMID: 35027846 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

