Drivers of Subjective Well-Being Under Different Economic Scenarios
- PMID: 34456812
- PMCID: PMC8386685
- DOI: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.696184
Drivers of Subjective Well-Being Under Different Economic Scenarios
Abstract
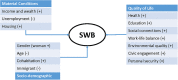
This paper explores the evolution of the driving forces that shape individual subjective well-being (SWB) in Spain from 2013 to 2018. Several socio-demographic, material conditions and quality of life (QoL) variables are considered as potential drivers of SWB. The data come from a large survey carried in two different time periods. The first one (2013) is characterized by a negative economic scenario as a result of the global financial crisis of 2008. The second one (2018) is characterized by fast economic recovery. Our results suggest that the material conditions variables, especially unemployment, have a much deeper impact on SWB during economic downturns than during economic recovery periods. Social connections and health status are determinant factors behind SWB, especially if the economy is working well. Our results also point to changes in gender effects. While women were happier than men in 2013, this effect disappears in 2018. Paradoxically, this suggest an increase in female expectations about their own lives during this period.
Keywords: Spain; economic downturn; life satisfaction; quality of life; subjective well-being.
Copyright © 2021 Arrondo, Cárcaba and González.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
This recession is wearing me out! Health-related quality of life and economic downturns.J Ment Health Policy Econ. 2011 Jun;14(2):61-72. J Ment Health Policy Econ. 2011. PMID: 21881162
-
Getting Old Well in Sub Saharan Africa: Exploring the Social and Structural Drivers of Subjective Wellbeing among Elderly Men and Women in Uganda.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020 Mar 31;17(7):2347. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17072347. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020. PMID: 32244270 Free PMC article.
-
How are the employed and unemployed affected by the economic crisis in Spain? Educational inequalities, life conditions and mental health in a context of high unemployment.BMC Public Health. 2016 Mar 15;16:267. doi: 10.1186/s12889-016-2934-z. BMC Public Health. 2016. PMID: 26979336 Free PMC article.
-
The Impact of Social Support and Pregnancy on Subjective Well-Being: A Systematic Review.Front Psychol. 2021 Sep 9;12:710858. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2021.710858. eCollection 2021. Front Psychol. 2021. PMID: 34566789 Free PMC article.
-
Personality, culture, and subjective well-being: emotional and cognitive evaluations of life.Annu Rev Psychol. 2003;54:403-25. doi: 10.1146/annurev.psych.54.101601.145056. Epub 2002 Jun 10. Annu Rev Psychol. 2003. PMID: 12172000 Review.
Cited by
-
Social Capital as a Predictor of Quality of Life: The Czech Experience.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022 May 19;19(10):6185. doi: 10.3390/ijerph19106185. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35627721 Free PMC article.
-
Les Misérables: An analysis of low SWB across the world.Front Psychol. 2023 Jun 8;14:1107939. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2023.1107939. eCollection 2023. Front Psychol. 2023. PMID: 37359886 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ambrey C., Fleming C. (2014). Public greenspace and life satisfaction in urban Australia. Urban Stud. 51 1290–1321. 10.1177/0042098013494417 - DOI
-
- Argyle M. (2013). The Psychology of Happiness. New York, NY: Routledge.
-
- Argyle M., Furnham A. (1983). Sources of satisfaction and conflict in long-term relationships. J. Marriage Fam. 45 481–493. 10.2307/351654 - DOI
-
- Arrondo R., Cárcaba A., González E. (2020). Drivers of subjective well-being in spain: are there gender differences? Appl. Res. Qual. Life 1–24. 10.4018/978-1-4666-3631-6.ch001 - DOI
-
- Avolio M. L., Pataki D. E., Pincetl S., Gillespie T. W., Jenerette G. D., McCarthy H. R. (2015). Understanding preferences for tree attributes: the relative effects of socio-economic and local environmental factors. Urban Ecosyst. 18 73–86. 10.1007/s11252-014-0388-6 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources