Hemodynamic Versus Anatomic Assessment of Symptomatic Atherosclerotic Middle Cerebral Artery Stenosis: the Relationship Between Pressure Wire Translesional Gradient and Angiographic Lesion Geometry
- PMID: 34456841
- PMCID: PMC8385769
- DOI: 10.3389/fneur.2021.671778
Hemodynamic Versus Anatomic Assessment of Symptomatic Atherosclerotic Middle Cerebral Artery Stenosis: the Relationship Between Pressure Wire Translesional Gradient and Angiographic Lesion Geometry
Abstract
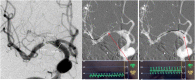
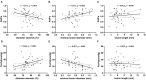
Background: Intracranial cerebral atherosclerosis (ICAS) is a leading etiology of ischemic stroke. The diagnosis and assessment of intracranial stenosis are shifting from anatomic to hemodynamic for better risk stratification. However, the relationships between lesion geometry and translesional pressure gradient have not been clearly elucidated. Methods: Patients with symptomatic unifocal M1 middle cerebral artery (M1-MCA) stenosis were consecutively recruited. The translesional pressure gradient was measured with a pressure wire and was recorded as both mean distal/proximal pressure ratios (Pd/Pa) and translesional pressure difference (Pa-Pd). Lesion geometry measured on angiography was recorded as diameter stenosis, minimal lumen diameter, and lesion length. The correlations between pressure-derived and angiography-derived indices were then analyzed. Results: Forty-three patients were analyzed. A negative correlation was found between Pd/Pa and diameter stenosis (r = -0.371; p = 0.014) and between Pa - Pd and minimal lumen diameter (r = -0.507; p = 0.001). A positive correlation was found between Pd/Pa and minimal lumen diameter (r = 0.411; p = 0.006) and between Pa - Pd and diameter stenosis (r = 0.466; p = 0.002). Conclusions: In a highly selected ICAS subgroup, geometric indices derived from angiography correlate significantly with translesional pressure gradient indices. However, the correlation strength is weak-to-moderate, which implies that anatomic assessment could only partly reflect hemodynamic status. Translesional pressure gradient measured by pressure wire may serve as a more predictive marker of ICAS severity. More factors need to be identified in further studies.
Keywords: Pa-Pd; Pd/Pa; hemodynamics; intracranial cerebral atherosclerosis; stenosis; translesional pressure gradient.
Copyright © 2021 Li, Yang, Dmytriw, Wang, Luo, Li, Ma, Chen, Wang, Gao, Feng, Bai, Zhang, Dong, Yang, Jiao and Ling.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest. The handling editor HQZ declared a shared affiliation, though no other collaboration, with one or more authors LL, BY, TW, JL, YL, YM, JC, YW, PG, YF, XB, XZ, JD, RY, LJ, FL at the time of the review.
Figures
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

