The Antimicrobial Activity of the AGXX® Surface Coating Requires a Small Particle Size to Efficiently Kill Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 34456898
- PMCID: PMC8387631
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2021.731564
The Antimicrobial Activity of the AGXX® Surface Coating Requires a Small Particle Size to Efficiently Kill Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
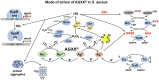
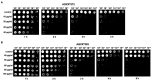
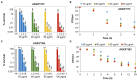
Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) isolates are often resistant to multiple antibiotics and pose a major health burden due to limited treatment options. The novel AGXX® surface coating exerts strong antimicrobial activity and successfully kills multi-resistant pathogens, including MRSA. The mode of action of AGXX® particles involves the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS), which induce an oxidative and metal stress response, increased protein thiol-oxidations, protein aggregations, and an oxidized bacillithiol (BSH) redox state in S. aureus. In this work, we report that the AGXX® particle size determines the effective dose and time-course of S. aureus USA300JE2 killing. We found that the two charges AGXX®373 and AGXX®383 differ strongly in their effective concentrations and times required for microbial killing. While 20-40 μg/ml AGXX®373 of the smaller particle size of 1.5-2.5 μm resulted in >99.9% killing after 2 h, much higher amounts of 60-80 μg/ml AGXX®383 of the larger particle size of >3.2 μm led to a >99% killing of S. aureus USA300JE2 within 3 h. Smaller AGXX® particles have a higher surface/volume ratio and therefore higher antimicrobial activity to kill at lower concentrations in a shorter time period compared to the larger particles. Thus, in future preparations of AGXX® particles, the size of the particles should be kept at a minimum for maximal antimicrobial activity.
Keywords: AGXX®; Staphylococcus aureus; antimicrobial activity; contact killing; metal particles.
Copyright © 2021 Linzner and Antelmann.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Boudreau M. D., Imam M. S., Paredes A. M., Bryant M. S., Cunningham C. K., Felton R. P., et al. (2016). Differential effects of silver nanoparticles and silver ions on tissue accumulation, distribution, and toxicity in the Sprague Dawley rat following daily oral gavage administration for 13 weeks. Toxicol. Sci. 150, 131–160. 10.1093/toxsci/kfv318, PMID: - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen J.-Y., Wang L.-Y., Wu P.-W. (2010). Preparation and characterization of ruthenium films via an electroless deposition route. Thin Solid Films 518, 7245–7248. 10.1016/j.tsf.2010.04.086 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

