Biomarkers of Inflammation and Inflammation-Related Indexes upon Emergency Department Admission Are Predictive for the Risk of Intensive Care Unit Hospitalization and Mortality in Acute Poisoning: A 6-Year Prospective Observational Study
- PMID: 34457088
- PMCID: PMC8390135
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/4696156
Biomarkers of Inflammation and Inflammation-Related Indexes upon Emergency Department Admission Are Predictive for the Risk of Intensive Care Unit Hospitalization and Mortality in Acute Poisoning: A 6-Year Prospective Observational Study
Abstract
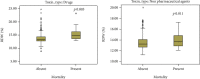
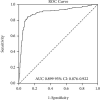
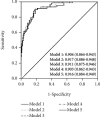
Patients poisoned with drugs and nonpharmaceutical substances are frequently admitted from the emergency department (ED) to a medical or ICU department. We hypothesized that biomarkers of inflammation and inflammation-related indexes based on the complete blood cell (CBC) count can identify acutely poisoned patients at increased risk for ICU hospitalization and death. We performed a 6-year prospective cohort study on 1548 adult patients. The demographic data, the levels of hs-CRP (high-sensitivity C-reactive protein), CBC, and inflammation-related indexes based on CBC counts were collected upon admission and compared between survivors and nonsurvivors, based on the poison involved. Both a multivariate logistic regression model with only significant univariate predictors and a model including univariate predictors plus each log-transformed inflammation-related indexes for mortality were constructed. The importance of the variables for mortality was graphically represented using the nomogram. hs-CRP (odds ratio (OR), 1.38; 95% CI, 1.16-1.65, p < 0.001 for log-transformed hs-CRP), red cell distribution width (RDW), neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR), and platelet-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) were significantly associated with the risk of ICU hospitalization, after multivariable adjustment. Only RDW, NLR, and monocyte-lymphocyte ratio (MLR) were significantly associated with mortality. The predictive accuracy for mortality of the models which included either NLR (AUC 0.917, 95% CI 0.886-0.948) or MLR (AUC 0.916, 95% CI 0.884-0.948) showed a high ability for prognostic detection. The use of hs-CRP, RDW, NLR, and MLR upon ED admission are promising screening tools for predicting the outcomes of patients acutely intoxicated with undifferentiated poisons.
Copyright © 2021 Catalina Lionte et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest regarding the publication of this paper.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Evaluation of prognostic values of inflammation-based makers in patients with HBV-related acute-on-chronic liver failure.Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Nov;97(46):e13324. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000013324. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018. PMID: 30431619 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison of the prognostic values of inflammation markers in patients with acute pancreatitis: a retrospective cohort study.BMJ Open. 2017 Mar 27;7(3):e013206. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2016-013206. BMJ Open. 2017. PMID: 28348184 Free PMC article.
-
Prognostic value of an inflammatory biomarker-based clinical algorithm in septic patients in the emergency department: An observational study.Int Immunopharmacol. 2020 Mar;80:106145. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2019.106145. Epub 2020 Jan 16. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020. PMID: 31955067
-
Prognostic value of systemic inflammation response indexes obtained from the complete blood count in patients treated for advanced ovarian carcinoma in front line.Clin Transl Oncol. 2024 Dec;26(12):3211-3217. doi: 10.1007/s12094-024-03523-3. Epub 2024 Jun 10. Clin Transl Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38856872 Free PMC article.
-
The role of inflammatory indices in the outcome of COVID-19 cancer patients.Med Oncol. 2021 Nov 8;39(1):6. doi: 10.1007/s12032-021-01605-8. Med Oncol. 2021. PMID: 34748094 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
The Value of Early and Follow-Up Elevated Scores Based on Peripheral Complete Blood Cell Count for Predicting Adverse Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients.J Pers Med. 2022 Dec 9;12(12):2037. doi: 10.3390/jpm12122037. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36556258 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Hematological Biomarkers of Inflammation with 10-Year Major Adverse Cardiovascular Events and All-Cause Mortality in Patients with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatotic Liver Disease: The ARIC Study.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Jul 2;17:4247-4256. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S466469. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 38973998 Free PMC article.
-
Gender Differences and Amputation Risk in Peripheral Artery Disease-A Single-Center Experience.Diagnostics (Basel). 2023 Oct 7;13(19):3145. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics13193145. Diagnostics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37835888 Free PMC article.
-
A nomogram proposal for early prediction of intensive care unit admission in patients with acute antipsychotic poisoning.Toxicol Res (Camb). 2023 Sep 19;12(5):873-883. doi: 10.1093/toxres/tfad078. eCollection 2023 Oct. Toxicol Res (Camb). 2023. PMID: 37915484 Free PMC article.
-
Electrocardiogram Features in Non-Cardiac Diseases: From Mechanisms to Practical Aspects.J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024 Apr 20;17:1695-1719. doi: 10.2147/JMDH.S445549. eCollection 2024. J Multidiscip Healthc. 2024. PMID: 38659633 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Dundar Z. D., Koylu R., Ergin M., Gunaydin Y. K., Ozer R., Cander B. Prognostic value of red cell distribution width in patients with organophosphate poisoning. Journal of Academic Emergency Medicine. 2015;14(2):65–69. doi: 10.5152/jaem.2015.90692. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

