Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Children With Chronic Kidney Disease: Impact of Apolipoprotein C-II and Apolipoprotein C-III
- PMID: 34458211
- PMCID: PMC8397580
- DOI: 10.3389/fped.2021.706323
Cardiovascular Disease Risk in Children With Chronic Kidney Disease: Impact of Apolipoprotein C-II and Apolipoprotein C-III
Abstract
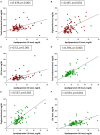
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) is an evolving process that begins in the early stages of chronic kidney disease (CKD) in children. Several surrogate markers, such as ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM), left ventricular (LV) mass, and arterial stiffness assessment, allow for the early detection of subclinical CVD in pediatric CKD. Four groups of plasma samples (n = 3/group) from congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract (CAKUT), as well as non-CAKUT patients with or without BP abnormalities, were studied to screen differentially expressed proteins using isobaric tags for relative and absolute protein quantification (iTRAQ)-based proteomics. As a result, 20 differentially expressed proteins associated with hypertension in children with CKD were discovered. Among them, apolipoprotein C-II (apoC-II) was found to have the highest abundance among the CKD patients with hypertension. As such, we hypothesized that apoC-II and apolipoprotein C-III (apoC-III) levels were related to BP abnormalities and CVD in children suffering from mild-to-moderate CKD. We examined their associations with surrogate markers of CV risk in 88 pediatric patients with CKD stages G1-G4. Children with CKD stages G2-G4 had a higher plasma apoC-II level than G1 patients (6.35 vs. 5.05 mg/dl, p < 0.05). We observed that ABPM abnormalities, LV mass, and arterial stiffness parameters were greater in CKD children who had stages G2-G4 than in those who had stage G1 (all p < 0.05). Plasma levels of apoC-II and apoC-III were positively correlated with total cholesterol, triglyceride, and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) (all p < 0.001). In multivariate linear regression analyses, apoC-II was correlated with a high LV mass index and an abnormal ABPM profile, and apoC-III was correlated with 24-h hypertension (r = 0.303, p = 0.003) and asleep hypertension (r = 0.379, p < 0.001). Early evaluations of apoC-II and apoC-III, ABPM, and surrogate markers of CV risk will aid in early preventative interventions to reduce the risk of CV in youths suffering from CKD.
Keywords: ambulatory blood pressure monitoring; apolipoprotein C; cardiovascular disease; children; chronic kidney disease; congenital anomalies of the kidney and urinary tract; hypertension; proteomics.
Copyright © 2021 Chen, Tain, Chen and Hsu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- GBD 2017 Risk Factor Collaborators. Global, regional, and national comparative risk assessment of 84 behavioural, environmental and occupational, and metabolic risks or clusters of risks for 195 countries and territories, 1990-2017: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. (2018) 392:1923–94. 10.1016/S0140-6736(18)32225-6 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

