Alternative Therapeutic Interventions: Antimicrobial Peptides and Small Molecules to Treat Microbial Keratitis
- PMID: 34458234
- PMCID: PMC8386189
- DOI: 10.3389/fchem.2021.694998
Alternative Therapeutic Interventions: Antimicrobial Peptides and Small Molecules to Treat Microbial Keratitis
Abstract
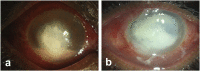
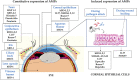
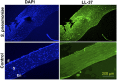
Microbial keratitis is a leading cause of blindness worldwide and results in unilateral vision loss in an estimated 2 million people per year. Bacteria and fungus are two main etiological agents that cause corneal ulcers. Although antibiotics and antifungals are commonly used to treat corneal infections, a clear trend with increasing resistance to these antimicrobials is emerging at rapid pace. Extensive research has been carried out to determine alternative therapeutic interventions, and antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are increasingly recognized for their clinical potential in treating infections. Small molecules targeted against virulence factors of the pathogens and natural compounds are also explored to meet the challenges and growing demand for therapeutic agents. Here we review the potential of AMPs, small molecules, and natural compounds as alternative therapeutic interventions for the treatment of corneal infections to combat antimicrobial resistance. Additionally, we have also discussed about the different formats of drug delivery systems for optimal administration of drugs to treat microbial keratitis.
Keywords: antimicrobial pepides; drug delivery systems; microbial keratitis; ocular surface; small molecules; wound healing.
Copyright © 2021 Jadi, Sharma, Bhogapurapu and Roy.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
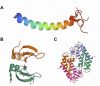
Similar articles
-
Novel Peptides with Dual Properties for Treating Pseudomonas aeruginosa Keratitis: Antibacterial and Corneal Wound Healing.Biomolecules. 2023 Jun 23;13(7):1028. doi: 10.3390/biom13071028. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37509064 Free PMC article.
-
Antimicrobial Peptide Expression at the Ocular Surface and Their Therapeutic Use in the Treatment of Microbial Keratitis.Front Microbiol. 2022 Jun 2;13:857735. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.857735. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35722307 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unlocking the Potential of Antimicrobial Peptides: Cutting-Edge Advances and Therapeutic Potential in Combating Bacterial Keratitis.Bioconjug Chem. 2025 Mar 19;36(3):311-331. doi: 10.1021/acs.bioconjchem.4c00594. Epub 2025 Feb 19. Bioconjug Chem. 2025. PMID: 39970053 Review.
-
Pythium Keratitis.2025 May 5. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. 2025 May 5. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2025 Jan–. PMID: 34424645 Free Books & Documents.
-
Advancements in peptide-based antimicrobials: A possible option for emerging drug-resistant infections.Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2024 Nov;333:103282. doi: 10.1016/j.cis.2024.103282. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Adv Colloid Interface Sci. 2024. PMID: 39276418 Review.
Cited by
-
Antimicrobial activity of cell-free supernatant derived from Ligilactobacillus animalis SWLA-1 in a novel ex vivo canine corneal infection model.Front Vet Sci. 2024 Apr 23;11:1346313. doi: 10.3389/fvets.2024.1346313. eCollection 2024. Front Vet Sci. 2024. PMID: 38716232 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Peptides with Dual Properties for Treating Pseudomonas aeruginosa Keratitis: Antibacterial and Corneal Wound Healing.Biomolecules. 2023 Jun 23;13(7):1028. doi: 10.3390/biom13071028. Biomolecules. 2023. PMID: 37509064 Free PMC article.
-
Novel treatment of infectious keratitis in canine corneas using ultraviolet C (UV-C) light.Vet Ophthalmol. 2025 Jul;28(4):699-713. doi: 10.1111/vop.13265. Epub 2024 Aug 8. Vet Ophthalmol. 2025. PMID: 39118265 Free PMC article.
-
An Overview of Frog Skin-Derived Esc Peptides: Promising Multifunctional Weapons against Pseudomonas aeruginosa-Induced Pulmonary and Ocular Surface Infections.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 16;25(8):4400. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084400. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38673985 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential expression of antimicrobial peptides in human fungal keratitis.Int J Ophthalmol. 2023 Oct 18;16(10):1630-1635. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2023.10.11. eCollection 2023. Int J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37854369 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

