Multifunctional Fructose 1,6-Bisphosphate Aldolase as a Therapeutic Target
- PMID: 34458323
- PMCID: PMC8385298
- DOI: 10.3389/fmolb.2021.719678
Multifunctional Fructose 1,6-Bisphosphate Aldolase as a Therapeutic Target
Abstract
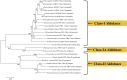
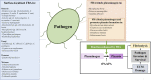
Fructose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolase is a ubiquitous cytosolic enzyme that catalyzes the fourth step of glycolysis. Aldolases are classified into three groups: Class-I, Class-IA, and Class-II; all classes share similar structural features but low amino acid identity. Apart from their conserved role in carbohydrate metabolism, aldolases have been reported to perform numerous non-enzymatic functions. Here we review the myriad "moonlighting" functions of this classical enzyme, many of which are centered on its ability to bind to an array of partner proteins that impact cellular scaffolding, signaling, transcription, and motility. In addition to the cytosolic location, aldolase has been found the extracellular surface of several pathogenic bacteria, fungi, protozoans, and metazoans. In the extracellular space, the enzyme has been reported to perform virulence-enhancing moonlighting functions e.g., plasminogen binding, host cell adhesion, and immunomodulation. Aldolase's importance has made it both a drug target and vaccine candidate. In this review, we note the several inhibitors that have been synthesized with high specificity for the aldolases of pathogens and cancer cells and have been shown to inhibit classical enzyme activity and moonlighting functions. We also review the many trials in which recombinant aldolases have been used as vaccine targets against a wide variety of pathogenic organisms including bacteria, fungi, and metazoan parasites. Most of such trials generated significant protection from challenge infection, correlated with antigen-specific cellular and humoral immune responses. We argue that refinement of aldolase antigen preparations and expansion of immunization trials should be encouraged to promote the advancement of promising, protective aldolase vaccines.
Keywords: aldolase; glycolysis; inhibitor; moonlighting function; vaccine.
Copyright © 2021 Pirovich, Da’dara and Skelly.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development of metal-chelating inhibitors for the Class II fructose 1,6-bisphosphate (FBP) aldolase.J Inorg Biochem. 2012 Jul;112:49-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2012.02.032. Epub 2012 Mar 10. J Inorg Biochem. 2012. PMID: 22546686
-
Exploring substrate binding and discrimination in fructose1, 6-bisphosphate and tagatose 1,6-bisphosphate aldolases.Eur J Biochem. 2000 Mar;267(6):1858-68. doi: 10.1046/j.1432-1327.2000.01191.x. Eur J Biochem. 2000. PMID: 10712619
-
Archaeal fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolases constitute a new family of archaeal type class I aldolase.J Biol Chem. 2001 Aug 3;276(31):28710-8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M103447200. Epub 2001 May 31. J Biol Chem. 2001. PMID: 11387336
-
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphate aldolase (FBA)-a conserved glycolytic enzyme with virulence functions in bacteria: 'ill met by moonlight'.Biochem Soc Trans. 2014 Dec;42(6):1792-5. doi: 10.1042/BST20140203. Biochem Soc Trans. 2014. PMID: 25399608 Review.
-
Diverse roles of aldolase enzymes in cancer development, drug resistance and therapeutic approaches as moonlighting enzymes.Med Oncol. 2024 Aug 9;41(9):224. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02470-x. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 39120781 Review.
Cited by
-
Generational Diet-Induced Obesity Remodels the Omental Adipose Proteome in Female Mice.Nutrients. 2024 Sep 13;16(18):3086. doi: 10.3390/nu16183086. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39339686 Free PMC article.
-
Is There a Difference in the Proteomic Profile of Stimulated and Unstimulated Saliva Samples from Pregnant Women with/without Obesity and Periodontitis?Cells. 2023 May 14;12(10):1389. doi: 10.3390/cells12101389. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37408223 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of moderate intensity exercise on liver metabolism in mice based on multi-omics analysis.Sci Rep. 2024 Dec 28;14(1):31072. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-82150-y. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39730655 Free PMC article.
-
Enolase of Staphylococcus lugdunensis Is a Surface-Exposed Moonlighting Protein That Binds to Extracellular Matrix and the Plasminogen/Plasmin System.Front Microbiol. 2022 Mar 3;13:837297. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.837297. eCollection 2022. Front Microbiol. 2022. PMID: 35308335 Free PMC article.
-
Host and bacterial urine proteomics might predict treatment outcomes for immunotherapy in advanced non-small cell lung cancer patients.Front Immunol. 2025 Apr 14;16:1543817. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2025.1543817. eCollection 2025. Front Immunol. 2025. PMID: 40297587 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

