Applications of Functionalized Hydrogels in the Regeneration of the Intervertebral Disc
- PMID: 34458364
- PMCID: PMC8397561
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/2818624
Applications of Functionalized Hydrogels in the Regeneration of the Intervertebral Disc
Abstract
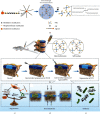
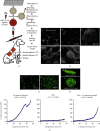
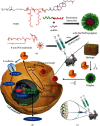
Intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) is caused by genetics, aging, and environmental factors and is one of the leading causes of low back pain. The treatment of IDD presents many challenges. Hydrogels are biomaterials that possess properties similar to those of the natural extracellular matrix and have significant potential in the field of regenerative medicine. Hydrogels with various functional qualities have recently been used to repair and regenerate diseased intervertebral discs. Here, we review the mechanisms of intervertebral disc homeostasis and degeneration and then discuss the applications of hydrogel-mediated repair and intervertebral disc regeneration. The classification of artificial hydrogels and natural hydrogels is then briefly introduced, followed by an update on the development of functional hydrogels, which include noncellular therapeutic hydrogels, cellular therapeutic hydrogel scaffolds, responsive hydrogels, and multifunctional hydrogels. The challenges faced and future developments of the hydrogels used in IDD are discussed as they further promote their clinical translation.
Copyright © 2021 Caiping Yan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
We declare that we do not have any commercial or associative interest that represents a conflict of interest in connection with the work submitted.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Research progress on intervertebral disc repair strategies and mechanisms based on hydrogel.J Biomater Appl. 2025 May;39(10):1121-1142. doi: 10.1177/08853282251320227. Epub 2025 Feb 10. J Biomater Appl. 2025. PMID: 39929142 Review.
-
In vivo biofunctional evaluation of hydrogels for disc regeneration.Eur Spine J. 2014 Jan;23(1):19-26. doi: 10.1007/s00586-013-2998-8. Eur Spine J. 2014. PMID: 24121748 Free PMC article.
-
Revolutionizing Intervertebral Disc Regeneration: Advances and Future Directions in Three-Dimensional Bioprinting of Hydrogel Scaffolds.Int J Nanomedicine. 2024 Oct 21;19:10661-10684. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S469302. eCollection 2024. Int J Nanomedicine. 2024. PMID: 39464675 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Strategies for regeneration of the intervertebral disc.Regen Med. 2008 Sep;3(5):717-29. doi: 10.2217/17460751.3.5.717. Regen Med. 2008. PMID: 18729796 Review.
-
Hydrogel based cartilaginous tissue regeneration: recent insights and technologies.Biomater Sci. 2017 Mar 28;5(4):613-631. doi: 10.1039/c6bm00863a. Biomater Sci. 2017. PMID: 28233881 Review.
Cited by
-
Cutting-Edge Biomaterials in Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Tissue Engineering.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jul 24;16(8):979. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16080979. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39204324 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Self-healing injectable multifunctional hydrogels for intervertebral disc disease.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Mar 11;32:101655. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101655. eCollection 2025 Jun. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40166378 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Deciphering the Effect of Hyaluronic Acid/Collagen Hydrogel for Pain Relief and Tissue Hydration in a Rat Model of Intervertebral Disc Degeneration.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Sep 11;16(18):2574. doi: 10.3390/polym16182574. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39339037 Free PMC article.
-
Application and development of hydrogel biomaterials for the treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration: a literature review.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023 Dec 7;11:1286223. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2023.1286223. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 38130952 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Recent advances in the repair of degenerative intervertebral disc for preclinical applications.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023 Sep 22;11:1259731. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2023.1259731. eCollection 2023. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 37811372 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- An H. S., Takegami K., Kamada H., et al. Intradiscal administration of osteogenic protein-1 increases intervertebral disc height and proteoglycan content in the nucleus pulposus in normal adolescent rabbits. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 2005;30(1):25–31. doi: 10.1097/01.brs.0000148002.68656.4d. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

