In vitro Histone H3 Cleavage Assay for Yeast and Chicken Liver H3 Protease
- PMID: 34458416
- PMCID: PMC8376558
- DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2085
In vitro Histone H3 Cleavage Assay for Yeast and Chicken Liver H3 Protease
Abstract
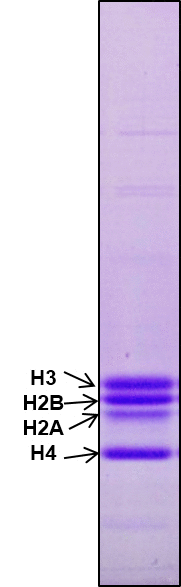
Histone proteins are subjected to a wide array of reversible and irreversible post-translational modifications (PTMs) (Bannister and Kouzarides, 2011; Azad and Tomar, 2014). The PTMs on histones are known to regulate chromatin structure and function. Histones are irreversibly modified by proteolytic clipping of their tail domains. The proteolytic clipping of histone tails is continuously attracting interest of researchers in the field of chromatin biology. We can recapitulate H3-clipping by performing in vitro H3 cleavage assay. Here, we are presenting the detailed protocol to perform in vitro H3 cleavage assay.
Keywords: Chicken liver H3 protease; Chromatin; Histone H3; Histone clipping; Yeast H3 protease.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Unexpected histone H3 tail-clipping activity of glutamate dehydrogenase.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jun 28;288(26):18743-57. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.462531. Epub 2013 May 14. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23673664 Free PMC article.
-
Biochemical Analysis Reveals the Multifactorial Mechanism of Histone H3 Clipping by Chicken Liver Histone H3 Protease.Biochemistry. 2016 Sep 27;55(38):5464-82. doi: 10.1021/acs.biochem.6b00625. Epub 2016 Sep 12. Biochemistry. 2016. PMID: 27586699
-
Partial purification of histone H3 proteolytic activity from the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Yeast. 2016 Jun;33(6):217-26. doi: 10.1002/yea.3153. Epub 2016 Apr 7. Yeast. 2016. PMID: 26833661
-
The micronuclear histone H3 clipping in the unicellular eukaryote Tetrahymena thermophila.Mar Life Sci Technol. 2022 Nov 24;4(4):584-594. doi: 10.1007/s42995-022-00151-0. eCollection 2022 Nov. Mar Life Sci Technol. 2022. PMID: 37078088 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Modifying Chromatin by Histone Tail Clipping.J Mol Biol. 2018 Sep 14;430(18 Pt B):3051-3067. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2018.07.013. Epub 2018 Jul 25. J Mol Biol. 2018. PMID: 30009770 Review.
References
-
- Azad G. K. and Tomar R. S.(2014). Proteolytic clipping of histone tails: the emerging role of histone proteases in regulation of various biological processes. Mol Biol Rep 41(5): 2717-2730. - PubMed
-
- Azad G. K. and Tomar R. S.(2016). Partial purification of histone H3 proteolytic activity from the budding yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae . Yeast 33(6): 217-226. - PubMed
-
- Chauhan S., Mandal P. and Tomar R. S.(2016). Biochemical analysis reveals the multifactorial mechanism of histone H3 clipping by chicken liver histone H3 protease. Biochemistry 55(38): 5464-5482. - PubMed
-
- Chauhan S. and Tomar R. S.(2016). Efficient expression and purification of biologically active human cystatin proteins. Protein Expr Purif 118: 10-17. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

