Determination of the Predatory Capability of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus HD100
- PMID: 34458487
- PMCID: PMC8376625
- DOI: 10.21769/BioProtoc.2177
Determination of the Predatory Capability of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus HD100
Abstract
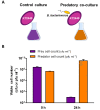
Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus HD100 is an obligate predator that preys upon a wide variety of Gram negative bacteria. The biphasic growth cycle of Bdellovibrio includes a free-swimming attack phase and an intraperiplasmic growth phase, where the predator replicates its DNA and grows using the prey as a source of nutrients, finally dividing into individual cells (Sockett, 2009). Due to its obligatory predatory lifestyle, manipulation of Bdellovibrio requires two-member culturing techniques using selected prey microorganisms ( Lambert et al., 2003 ). In this protocol, we describe a detailed workflow to grow and quantify B. bacteriovorus HD100 and its predatory ability, to easily carry out these laborious and time-consuming techniques.
Keywords: Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus; Predatory bacteria; Predatory quantification.
Copyright © 2017 The Authors; exclusive licensee Bio-protocol LLC.
Figures


References
-
- Atterbury R. J., Hobley L., Till R., Lambert C., Capeness M. J., Lerner T. R., Fenton A. K., Barrow P. and Sockett R. E.(2011). Effects of orally administered Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus on the well-being and Salmonella colonization of young chicks . Appl Environ Microbiol 77(16): 5794-5803. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Davidov Y. and Jurkevitch E.(2009). Predation between prokaryotes and the origin of eukaryotes. Bioessays 31(7): 748-757. - PubMed
-
- Gophna U., Charlebois R. L. and Doolittle W. F.(2006). Ancient lateral gene transfer in the evolution of Bdellovibrio bacteriovorus . Trends Microbiol 14(2): 64-69. - PubMed
-
- Jurkevitch E. and Davidov Y.(2007). Phylogenetic diversity and evolution of predatory prokaryotes. In: Jurkevitch, E.(Ed.). Microbiol Monogr Predatory Prokaryotes Heidelberg. Springer, pp: 11-56.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

