Synthesis, single crystal (XRD), Hirshfeld surface analysis, computational study (DFT) and molecular docking studies of (E)-4-((2-hydroxy-3,5-diiodobenzylidene)amino)-N-(pyrimidine)-2-yl) benzenesulfonamide
- PMID: 34458601
- PMCID: PMC8379672
- DOI: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2021.e07724
Synthesis, single crystal (XRD), Hirshfeld surface analysis, computational study (DFT) and molecular docking studies of (E)-4-((2-hydroxy-3,5-diiodobenzylidene)amino)-N-(pyrimidine)-2-yl) benzenesulfonamide
Abstract
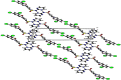
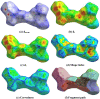
The Schiff base (E)-4-((2-hydroxy-3,5-diiodobenzylidene)amino)-N-(pyrimidine)-2-yl) benzene sulfonamide (DIDA) compound was synthesis with condensation of 3,5-diiodosalicylaldehyde and sulfadiazine. The compound characterized with FTIR, X-ray crystallography and electronic spectra. The titled compound associated with experimental and theoretical method, DFT used for the theoretical method. The IR was calculated from DFT mode with B3LYP/GENSEP basic set. The electronic spectra computed from TD-DFT method with CAM-B3LYP functional, with IEFPCM solvation model and DMSO used as the solvent. Wave function based properties like localized orbital locator, electron localization function and non-covalent interactions have been studied extensively. The ADMET properties of the compound DIDA indicated that the compound has excellent drug likeness properties and PASS studies showed that it has anti-infective properties, which is confirmed by a docking score of -7.4 kcal/mol.
Keywords: DFT; Drug-likeness; Molecular docking; Single crystal; Sulfadiazine; Synthesis.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
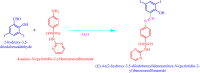
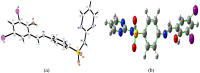
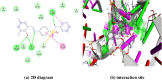
Similar articles
-
Synthesis, quantum chemical calculations, in silico and in vitro bioactivity of a sulfonamide-Schiff base derivative.Heliyon. 2024 Jul 14;10(14):e34556. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e34556. eCollection 2024 Jul 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39082025 Free PMC article.
-
Single crystal XRD, DFT investigations and molecular docking study of 2- ((1,5-dimethyl-3-oxo-2-phenyl-2,3-dihydro-1H-pyrazol-4-yl)amino)naphthalene-1,4-dione as a potential anti- cancer lead molecule.Comput Biol Chem. 2019 Feb;78:153-164. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiolchem.2018.11.022. Epub 2018 Nov 30. Comput Biol Chem. 2019. PMID: 30530296
-
A possible potential COVID-19 drug candidate: Diethyl 2-(2-(2-(3-methyl-2-oxoquinoxalin-1(2H)-yl)acetyl)hydrazono)malonate: Docking of disordered independent molecules of a novel crystal structure, HSA/DFT/XRD and cytotoxicity.Arab J Chem. 2022 Feb;15(2):103595. doi: 10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103595. Epub 2021 Nov 28. Arab J Chem. 2022. PMID: 34909067 Free PMC article.
-
Design, synthesis and spectroscopic and structural characterization of novel N-(2-hydroxy-5-methylphenyl)-2,3-dimethoxybenzamide: DFT, Hirshfeld surface analysis, antimicrobial activity, molecular docking and toxicology.Acta Crystallogr C Struct Chem. 2022 Sep 1;78(Pt 9):493-506. doi: 10.1107/S2053229622008257. Epub 2022 Aug 26. Acta Crystallogr C Struct Chem. 2022. PMID: 36063377
-
Experimental (XRD, FT-IR and UV-Vis) and theoretical modeling studies of Schiff base (E)-N'-((5-nitrothiophen-2-yl)methylene)-2-phenoxyaniline.Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2014 Jan 24;118:672-82. doi: 10.1016/j.saa.2013.08.054. Epub 2013 Aug 28. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc. 2014. PMID: 24096063
Cited by
-
Versatile photocatalytic activities of indenoquinoxalines for dye reduction, single-crystal nucleation, and MNP formation with iron scrap under sunlight.RSC Adv. 2024 Dec 4;14(52):38426-38458. doi: 10.1039/d4ra04808c. eCollection 2024 Dec 3. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 39635365 Free PMC article.
-
Spectroscopic characterization, DFT, antimicrobial activity and molecular docking studies on 4,5-bis[(E)-2-phenylethenyl]-1H,1'H-2,2'-biimidazole.Heliyon. 2024 Apr 16;10(9):e29566. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29566. eCollection 2024 May 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38707390 Free PMC article.
-
Deploying a Novel Approach to Prepare Silver Nanoparticle Bellamya bengalensis Extract Conjugate Coating on Orthopedic Implant Biomaterial Discs to Prevent Potential Biofilm Formation.Antibiotics (Basel). 2023 Sep 3;12(9):1403. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics12091403. Antibiotics (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37760700 Free PMC article.
-
Synthesis, solvent role, absorption and emission studies of cytosine derivative.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 26;10(7):e28623. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e28623. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38590870 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Gadad A.K., Mahajanshetti C.S., Nimbalkar S., Raichurkar A. Synthesis and an- tibacterial activity of some 5-guanylhydrazone/thiocyanato-6-arylimidazo[2,1- b ]-1,3, 4-thiadiazole-2-sulfonamide derivatives. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2000;35:853–857. - PubMed
-
- Maren T.H. Relatons between structure and biological activity of sulfonamides. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 1976;16:309–327. - PubMed
-
- Banuppriya G., Sribalan R., Padmini V. Synthesis and characterization of cur- cumin-sulfonamide hybrids: biological evaluation and molecular docking stud- ies. J. Mol. Struct. 2018;1155:90–100.
-
- Humphries P.S., Bersot R., Kincaid J., Mabery E., McCluskie K., Park T., Ren- ner T., Riegler E., Steinfeld T., Turtle E.D., Wei Z.L., Willis E. Carbazole-containing sulfonamides and sulfamides: discovery of cryptochrome modulators as antidi- abetic agents. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2016;26:757–760. - PubMed
-
- Sun L., Wu Y., Liu Y., Chen X., Hu L. Novel carbazole sulfonamide derivatives of antitumor agent: synthesis, antiproliferative activity and aqueous solubility. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2017;27:261–265. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

