High-frequency Multiphase 4DCT for the Detection of Parathyroid Adenomas: A Pictorial Essay
- PMID: 34458658
- PMCID: PMC8389182
- DOI: 10.1210/jendso/bvab132
High-frequency Multiphase 4DCT for the Detection of Parathyroid Adenomas: A Pictorial Essay
Abstract
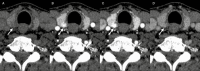
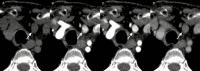
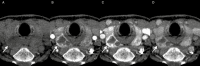
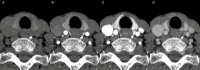
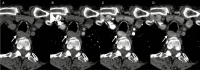
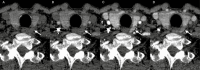
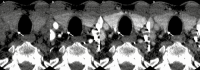
4-Dimensional computed tomography (4DCT) for the detection of (an) enlarged parathyroid(s) is a commonly performed examination in the management of primary hyperparathyroidism. In our center, we introduced a high-frequency multiphase 4DCT protocol obtaining 16 phases, including 11 different arterial phases. Exposure to this multiphase 4DCT technique is similar to that for classic helical 4DCT. In this pictorial essay we reconstructed our multiphase 4DCT series in the manner of a classic helical 4DCT and compare both techniques. We illustrate how multiphase 4DCT may aid in the detection of parathyroid adenomas. We found 17 out of 19 lesions demonstrating a type A pattern of enhancement, therefore suggesting this pattern could be more prevalent than previously thought. Some parathyroid adenomas may be mistaken for enlarged lymph nodes using classic 4DCT whereas high-frequency multiphase 4DCT can detect a temporary rise in enhancement, thus suggesting the lesions in question to be of parathyroid origin. Smaller lesions may prove more obvious as the difference in enhancement between parathyroid and thyroid can become more prominent.
Key point: Using high-frequency multiphase 4DCT an arterial phase with maximum enhancement of parathyroid tissue can be defined. This phase may aid in the detection of parathyroid adenomas.
Keywords: 4DCT; Primary hyperparathyroidism; multiphase scanning; parathyroid adenoma.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of the Endocrine Society.
Figures
References
-
- Rodgers SE, Hunter GJ, Hamberg LM, et al. . Improved preoperative planning for directed parathyroidectomy with 4-dimensional computed tomography. Surgery. 2006;140(6):932-940; discussion 940. - PubMed
-
- Bahl M, Sepahdari AR, Sosa JA, Hoang JK. Parathyroid adenomas and hyperplasia on four-dimensional CT scans: three patterns of enhancement relative to the thyroid gland justify a three-phase protocol. Radiology. 2015;277(2):454-462. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
