Antiapoptotic and antioxidative effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles on the testicular tissues of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: An experimental study
- PMID: 34458667
- PMCID: PMC8387707
- DOI: 10.18502/ijrm.v19i7.9465
Antiapoptotic and antioxidative effects of cerium oxide nanoparticles on the testicular tissues of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: An experimental study
Abstract
Background: Cerium dioxide nanoparticles (CNPs) due to the antidiabetic and antioxidant activities are proposed for the treatment of oxidative stress-associated diseases.
Objective: To examine the impact of CNPs on hyperglycemia-induced apoptosis and oxidative stress in the testis of diabetic rats.
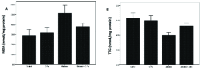
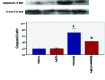
Materials and methods: Twenty-four male rats were divided into four groups (n = 6/each) as diabetic rats, CNPs group, diabetic + CNPs rats, and controls. The control group was fed only mouse food and water. Rats became diabetic through receiving streptozotocin (STZ) 60 mg/kg. CNPs were given to the rats at a dose of 30 mg/kg daily for 2 wk. Malondialdehyde and total thiol group (TTG) levels were measured using spectrofluorometer. Expression of b-cell lymphoma protein 2-associated X protein (BAX) and b-cell lymphoma protein 2 (Bcl-2) were investigated using quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction. Western blot analysis was used to examine caspase 3 protein levels.
Results: The content of malondialdehyde significantly increased in the STZ-diabetic rats, while TTG levels demonstrated a remarkable decrease. Caspase-3, BAX, and BAX/Bcl-2 mRNA ratio raised significantly in the STZ-diabetic rats. On the other hand, Bcl-2 mRNA levels reduced in the testis of diabetic rats (p = 0.006). Intervention with CNPs caused a substantial increase in the TTG levels, while the malondialdehyde contents, caspase-3, BAX levels, as well as BAX/Bcl-2 mRNA ratio were considerably decreased following CNPs treatment. Administration of CNPs increased mRNA levels of Bcl-2 (p 0.0001).
Conclusion: CNPs treatment attenuates testicular apoptosis and oxidative stress induced by diabetes. This nanoparticle might be suggested for the treatment of diabetes-associated reproductive disorders.
Keywords: Nanoceria; Oxidative stress; Apoptosis; Diabetes; Testis..
Copyright © 2021 Solgi et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Cai L, Chen S, Evans T, Deng DX, Mukherjee K, Chakrabarti S. Apoptotic germ-cell death and testicular damage in experimental diabetes: Prevention by endothelin antagonism. Urol Res. 2000;28:342–347. - PubMed
-
- Huang X, Shi X, Zhou J, Li S, Zhang L, Zhao H, et al. The activation of antioxidant and apoptosis pathways involved in damage of human proximal tubule epithelial cells by PM 2. 5 exposure Environ Sci Eur. 2020;32:1–3.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
