Fluorescent proteins of the EosFP clade: intriguing marker tools with multiple photoactivation modes for advanced microscopy
- PMID: 34458811
- PMCID: PMC8341165
- DOI: 10.1039/d1cb00014d
Fluorescent proteins of the EosFP clade: intriguing marker tools with multiple photoactivation modes for advanced microscopy
Abstract
Optical fluorescence microscopy has taken center stage in the exploration of biological structure and dynamics, especially on live specimens, and super-resolution imaging methods continue to deliver exciting new insights into the molecular foundations of life. Progress in the field, however, crucially hinges on advances in fluorescent marker technology. Among these, fluorescent proteins (FPs) of the GFP family are advantageous because they are genetically encodable, so that live cells, tissues or organisms can produce these markers all by themselves. A subclass of them, photoactivatable FPs, allow for control of their fluorescence emission by light irradiation, enabling pulse-chase imaging and super-resolution microscopy. In this review, we discuss FP variants of the EosFP clade that have been optimized by amino acid sequence modification to serve as markers for various imaging techniques. In general, two different modes of photoactivation are found, reversible photoswitching between a fluorescent and a nonfluorescent state and irreversible green-to red photoconversion. First, we describe their basic structural and optical properties. We then summarize recent research aimed at elucidating the photochemical processes underlying photoactivation. Finally, we briefly introduce various advanced imaging methods facilitated by specific EosFP variants, and show some exciting sample applications.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
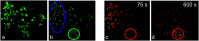
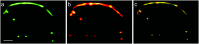
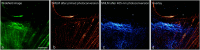
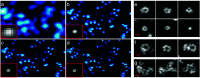


Similar articles
-
Genetically encodable fluorescent protein markers in advanced optical imaging.Methods Appl Fluoresc. 2022 Jul 28;10(4). doi: 10.1088/2050-6120/ac7d3f. Methods Appl Fluoresc. 2022. PMID: 35767981 Review.
-
A detailed review of genetically encodable RFPs and far-RFPs and their applications in advanced super-resolution imaging techniques.Biophys Chem. 2025 Jul;322:107432. doi: 10.1016/j.bpc.2025.107432. Epub 2025 Mar 15. Biophys Chem. 2025. PMID: 40117991 Review.
-
From EosFP to mIrisFP: structure-based development of advanced photoactivatable marker proteins of the GFP-family.J Biophotonics. 2011 Jun;4(6):377-90. doi: 10.1002/jbio.201000122. Epub 2011 Feb 14. J Biophotonics. 2011. PMID: 21319305 Review.
-
A photoactivatable marker protein for pulse-chase imaging with superresolution.Nat Methods. 2010 Aug;7(8):627-30. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1477. Epub 2010 Jul 4. Nat Methods. 2010. PMID: 20601949
-
Fluorescent proteins for live-cell imaging with super-resolution.Chem Soc Rev. 2014 Feb 21;43(4):1088-106. doi: 10.1039/c3cs60171d. Chem Soc Rev. 2014. PMID: 24056711 Review.
Cited by
-
A Photoactivatable Plasma Membrane Probe Based on a Self-Triggered Photooxidation Cascade for Live Cell Super-Resolution Microscopy.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025 Jun 10;64(24):e202425276. doi: 10.1002/anie.202425276. Epub 2025 Apr 21. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2025. PMID: 40192285 Free PMC article.
-
Uptake of small extracellular vesicles by recipient cells is facilitated by paracrine adhesion signaling.Nat Commun. 2025 Mar 12;16(1):2419. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-57617-9. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40075063 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetic isotope effect reveals rate-limiting step in green-to-red photoconvertible fluorescent proteins.Protein Sci. 2024 Jul;33(7):e5069. doi: 10.1002/pro.5069. Protein Sci. 2024. PMID: 38864740 Free PMC article.
-
Caveolae disassemble upon membrane lesioning and foster cell survival.iScience. 2024 Jan 9;27(2):108849. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2024.108849. eCollection 2024 Feb 16. iScience. 2024. PMID: 38303730 Free PMC article.
-
Decoding mEos4b day-long maturation and engineering fast-maturing variants.Protein Sci. 2025 Aug;34(8):e70234. doi: 10.1002/pro.70234. Protein Sci. 2025. PMID: 40671276 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Fluorescence Microscopy: From Principles to Biological Applications, ed. U. Kubitscheck, Wiley-VCH GmbH, Weinheim, Germany, 2017
-
- Stockert J. C. and Blazquez-Castro A., Fluorescence Microscopy in Life Sciences, ed. U. A. E. Sharjah, Bentham Science Publishers, 2017
-
- Far-Field Optical Nanoscopy, ed. P. Tinnefeld, C. Eggeling and S. W. Hell, Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2015
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

