Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus using BCMA-CD19 Compound CAR
- PMID: 34458965
- PMCID: PMC8599262
- DOI: 10.1007/s12015-021-10251-6
Treatment of Systemic Lupus Erythematosus using BCMA-CD19 Compound CAR
Conflict of interest statement
Y.M. is a cofounder of iCell Gene Therapeutics, LLC. All other authors report no conflict of interest.
Figures
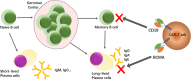
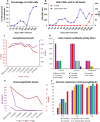
References
-
- Alexander T, Thiel A, Rosen O, Massenkeil G, Sattler A, Kohler S, et al. Depletion of autoreactive immunologic memory followed by autologous hematopoietic stem cell transplantation in patients with refractory SLE induces long-term remission through de novo generation of a juvenile and tolerant immune system. Blood. 2009;113(1):214–223. doi: 10.1182/blood-2008-07-168286. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Wang B, Yamamoto Y, El-Badri NS, Good RA. Effective treatment of autoimmune disease and progressive renal disease by mixed bone-marrow transplantation that establishes a stable mixed chimerism in BXSB recipient mice. Proceedings of the National academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 1999;96(6):3012–3016. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.6.3012. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Fang L, Hongyu Z, Xiao W, Xiong Y, Cao Y, Su Y, et al. First-in-Human Trial of Bcma-CD19 Compound CAR with Remarkable Donor-Specific Antibody Reduction. Blood. 2019;134(Supplement_1):38. doi: 10.1182/blood-2019-122964. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

