Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in patients with uncontrolled severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps and a clinical diagnosis of NSAID-ERD: Results from two randomized placebo-controlled phase 3 trials
- PMID: 34459002
- PMCID: PMC9292324
- DOI: 10.1111/all.15067
Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in patients with uncontrolled severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps and a clinical diagnosis of NSAID-ERD: Results from two randomized placebo-controlled phase 3 trials
Abstract
Background: About one-tenth of patients with difficult-to-treat chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) have comorbid non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-exacerbated respiratory disease (NSAID-ERD). Dupilumab, a fully human monoclonal antibody that blocks the shared interleukin (IL)-4/IL-13 receptor component, is an approved add-on treatment in severe CRSwNP. This post hoc analysis evaluated dupilumab efficacy and safety in patients with CRSwNP with/without NSAID-ERD.
Methods: Data were pooled from the phase 3 SINUS-24 and SINUS-52 studies in adults with uncontrolled severe CRSwNP who received dupilumab 300 mg or placebo every 2 weeks. CRSwNP, nasal airflow, lung function, and asthma control outcomes at Week 24 were evaluated, and treatment-subgroup interactions were assessed for patients with and without NSAID-ERD.
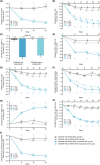
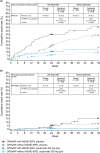
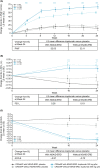
Results: Of 724 patients, 204 (28.2%) had a diagnosis of NSAID-ERD. At Week 24, least squares mean treatment differences demonstrated significant improvements in nasal polyp score, nasal congestion (NC), Lund-Mackay computed tomography, 22-item Sinonasal Outcome Test (SNOT-22), Total Symptom Score (TSS), rhinosinusitis severity visual analog scale, peak nasal inspiratory flow (PNIF), six-item Asthma Control Questionnaire score, and improvement in smell with dupilumab versus placebo (all p < .0001) in patients with NSAID-ERD. Treatment comparisons demonstrated significantly greater improvements with dupilumab in patients with versus without NSAID-ERD for NC (p = .0044), SNOT-22 (p = .0313), TSS (p = .0425), and PNIF (p = .0123).
Conclusions: In patients with uncontrolled severe CRSwNP, dupilumab significantly improved objective measures and patient-reported symptoms to a greater extent in the presence of comorbid NSAID-ERD than without. Dupilumab was well tolerated in patients with/without NSAID-ERD.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02912468 NCT02898454.
Keywords: IL-13; IL-4; chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps; dupilumab; non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug-exacerbated respiratory disease.
© 2021 Sanofi Genzyme. Allergy published by European Academy of Allergy and Clinical Immunology and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Efficacy and safety of dupilumab in patients with severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (LIBERTY NP SINUS-24 and LIBERTY NP SINUS-52): results from two multicentre, randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, parallel-group phase 3 trials.Lancet. 2019 Nov 2;394(10209):1638-1650. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(19)31881-1. Epub 2019 Sep 19. Lancet. 2019. PMID: 31543428 Clinical Trial.
-
Two-Year Data of Tapered Dupilumab Shows High Effectiveness in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps With Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drug-Exacerbated Respiratory Disease.Allergy. 2025 Jun;80(6):1737-1745. doi: 10.1111/all.16579. Epub 2025 May 16. Allergy. 2025. PMID: 40377347 Free PMC article.
-
Dupilumab Improves Outcomes in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps and Coexisting Asthma Irrespective of Baseline Asthma Characteristics.J Asthma Allergy. 2023 Apr 18;16:411-419. doi: 10.2147/JAA.S391896. eCollection 2023. J Asthma Allergy. 2023. PMID: 37096015 Free PMC article.
-
Dupilumab: A Review in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps.Drugs. 2020 May;80(7):711-717. doi: 10.1007/s40265-020-01298-9. Drugs. 2020. PMID: 32240527 Review.
-
Efficacy of Biologics in NSAID-ERD: United Airways From the Nose to the Bronchi.J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2024 Nov;12(11):2917-2932. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2024.09.021. Epub 2024 Sep 27. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2024. PMID: 39343299 Review.
Cited by
-
Dupilumab improves outcomes in patients with chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps irrespective of gender: results from the SINUS-52 trial.Clin Transl Immunology. 2024 Jun 8;13(6):e1511. doi: 10.1002/cti2.1511. eCollection 2024. Clin Transl Immunology. 2024. PMID: 38854740 Free PMC article.
-
Should Biologics Be Used Before Aspirin Desensitization in Aspirin-Exacerbated Respiratory Disease?J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2024 Jan;12(1):79-84. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2023.09.019. Epub 2023 Sep 29. J Allergy Clin Immunol Pract. 2024. PMID: 37778627 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Aspirin-exacerbated respiratory disease: Updates in the era of biologics.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2023 Sep;131(3):317-324. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2023.05.016. Epub 2023 May 22. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2023. PMID: 37225000 Free PMC article. Review.
-
An Analysis of Biologic Therapies in Patients With Asthma and Chronic Rhinosinusitis.Cureus. 2022 Oct 7;14(10):e30017. doi: 10.7759/cureus.30017. eCollection 2022 Oct. Cureus. 2022. PMID: 36225247 Free PMC article.
-
[Expert consensus on the diagnosis and treatment of respiratory diseases exacerbated by nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (2024, Chengdu)].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Jun;38(6):453-462. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2024.06.001. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38858107 Free PMC article. Chinese.
References
-
- Bachert C, Marple B, Schlosser RJ, et al. Adult chronic rhinosinusitis. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2020;6:86. - PubMed
-
- Fokkens WJ, Lund VJ, Hopkins C, et al. Epos 2020: European position paper on rhinosinusitis and nasal polyps 2020. Rhinology 2020;58:1‐464. - PubMed
-
- Klonaris D, Doulaptsi M, Karatzanis A, Velegrakis S, Milioni A, Prokopakis E. Assessing quality of life and burden of disease in chronic rhinosinusitis: A review. Rhinology Online 2019;2:6‐13.
-
- Bachert C, Han JK, Wagenmann M, et al. EUFOREA expert board meeting on uncontrolled severe chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) and biologics: Definitions and management. J Allergy Clin Immunol 2021;147:29‐36. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

