Dynamic EMT: a multi-tool for tumor progression
- PMID: 34459003
- PMCID: PMC8441439
- DOI: 10.15252/embj.2021108647
Dynamic EMT: a multi-tool for tumor progression
Abstract
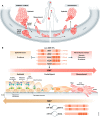
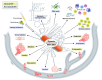
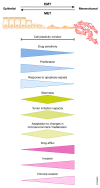
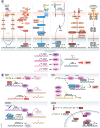
The process of epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) is fundamental for embryonic morphogenesis. Cells undergoing it lose epithelial characteristics and integrity, acquire mesenchymal features, and become motile. In cancer, this program is hijacked to confer essential changes in morphology and motility that fuel invasion. In addition, EMT is increasingly understood to orchestrate a large variety of complementary cancer features, such as tumor cell stemness, tumorigenicity, resistance to therapy and adaptation to changes in the microenvironment. In this review, we summarize recent findings related to these various classical and non-classical functions, and introduce EMT as a true tumorigenic multi-tool, involved in many aspects of cancer. We suggest that therapeutic targeting of the EMT process will-if acknowledging these complexities-be a possibility to concurrently interfere with tumor progression on many levels.
Keywords: EMT; MET; SLUG; SNAIL; TWIST; ZEB1; ZEB2; cancer; cell plasticity; hybrid EMT; invasion; metastasis; partial EMT; signaling pathways; tumor stemness.
© 2021 The Authors. Published under the terms of the CC BY 4.0 license.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Ahmed N, Maines‐Bandiera S, Quinn MA, Unger WG, Dedhar S, Auersperg N (2006) Molecular pathways regulating EGF‐induced epithelio‐mesenchymal transition in human ovarian surface epithelium. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 290: C1532–1542 - PubMed
-
- Akalay I, Janji B, Hasmim M, Noman MZ, André F, De Cremoux P, Bertheau P, Badoual C, Vielh P, Larsen AKet al (2013) Epithelial‐to‐mesenchymal transition and autophagy induction in breast carcinoma promote escape from T‐cell‐mediated lysis. Cancer Res 73: 2418–2427 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

