Differential protein expression during growth on model and commercial mixtures of naphthenic acids in Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf-5
- PMID: 34459546
- PMCID: PMC8289671
- DOI: 10.1002/mbo3.1196
Differential protein expression during growth on model and commercial mixtures of naphthenic acids in Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf-5
Abstract
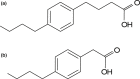
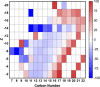
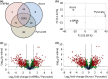
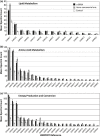
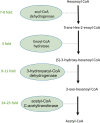
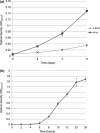
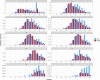
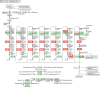
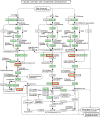
Naphthenic acids (NAs) are carboxylic acids with the formula (Cn H2n+Z O2 ) and are among the most toxic, persistent constituents of oil sands process-affected waters (OSPW), produced during oil sands extraction. Currently, the proteins and mechanisms involved in NA biodegradation are unknown. Using LC-MS/MS shotgun proteomics, we identified proteins overexpressed during the growth of Pseudomonas fluorescens Pf-5 on a model NA (4'-n-butylphenyl)-4-butanoic acid (n-BPBA) and commercial NA mixture (Acros). By day 11, >95% of n-BPBA was degraded. With Acros, a 17% reduction in intensity occurred with 10-18 carbon compounds of the Z family -2 to -14 (major NA species in this mixture). A total of 554 proteins (n-BPBA) and 631 proteins (Acros) were overexpressed during growth on NAs, including several transporters (e.g., ABC transporters), suggesting a cellular protective response from NA toxicity. Several proteins associated with fatty acid, lipid, and amino acid metabolism were also overexpressed, including acyl-CoA dehydrogenase and acyl-CoA thioesterase II, which catalyze part of the fatty acid beta-oxidation pathway. Indeed, multiple enzymes involved in the fatty acid oxidation pathway were upregulated. Given the presumed structural similarity between alkyl-carboxylic acid side chains and fatty acids, we postulate that P. fluorescens Pf-5 was using existing fatty acid catabolic pathways (among others) during NA degradation.
Keywords: Pseudomonas fluorescens; naphthenic acids; oil sands process-affected water; proteomics; tailing ponds; toxicity.
© 2021 The Authors. MicrobiologyOpen published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Ahad, J. M. E. , Pakdel, H. , Gammon, P. R. , Siddique, T. , Kuznetsova, A. , & Savard, M. M. (2018). Evaluating in situ biodegradation of 13C‐labelled naphthenic acids in groundwater near oil sands tailings ponds. Science of the Total Environment, 643, 392–399. - PubMed
-
- Alharbi, H. , Saunders, D. M. , Al‐Mousa, A. , Alcorn, J. , Pereira, A. S. , Martin, J. W. , Giesey, J. P. , & Wiseman, S. B. (2016). Inhibition of ABC transport proteins by oil sands process affected water. Aquatic Toxicology, 170, 81–88. - PubMed
-
- Alldridge, L. , Metodieva, G. , Greenwood, C. , Al‐Janabi, K. , Thwaites, L. , Sauven, P. , & Metodiev, M. (2008). Proteome profiling of breast tumors by gel electrophoresis and nano‐scale electrospray ionization mass spectrometry. Journal of Proteome Research, 7, 1458–1469. - PubMed
-
- Allesen‐Holm, M. , Barken, K. B. , Yang, L. , Klausen, M. , Webb, J. S. , Kjelleberg, S. , Molin, S. , Givskov, M. , & Tolker‐Nielsen, T. (2006). A characterization of DNA release in Pseudomonas aeruginosa cultures and biofilms. Molecular Microbiology, 59, 1114–1128. - PubMed
-
- Altschul, S. F. , Gish, W. , Miller, W. , Myers, E. W. , & Lipman, D. J. (1990). Basic local alignment search tool. Journal of Molecular Biology, 215, 403–410. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

