TGFβ signalling is required to maintain pluripotency of human naïve pluripotent stem cells
- PMID: 34463252
- PMCID: PMC8410071
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.67259
TGFβ signalling is required to maintain pluripotency of human naïve pluripotent stem cells
Abstract
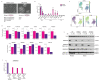
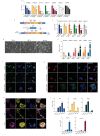
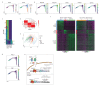
The signalling pathways that maintain primed human pluripotent stem cells (hPSCs) have been well characterised, revealing a critical role for TGFβ/Activin/Nodal signalling. In contrast, the signalling requirements of naive human pluripotency have not been fully established. Here, we demonstrate that TGFβ signalling is required to maintain naive hPSCs. The downstream effector proteins - SMAD2/3 - bind common sites in naive and primed hPSCs, including shared pluripotency genes. In naive hPSCs, SMAD2/3 additionally bind to active regulatory regions near to naive pluripotency genes. Inhibiting TGFβ signalling in naive hPSCs causes the downregulation of SMAD2/3-target genes and pluripotency exit. Single-cell analyses reveal that naive and primed hPSCs follow different transcriptional trajectories after inhibition of TGFβ signalling. Primed hPSCs differentiate into neuroectoderm cells, whereas naive hPSCs transition into trophectoderm. These results establish that there is a continuum for TGFβ pathway function in human pluripotency spanning a developmental window from naive to primed states.
Keywords: embryonic stem cells; gene regulation; human; pluripotent stem cells; regenerative medicine; stem cells.
© 2021, Osnato et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AO, SB, CK, SA, AC, SN, MQ, BW, DM, AB, KN, LV, DO, PR No competing interests declared
Figures









References
-
- Battle SL, Doni Jayavelu N, Azad RN, Hesson J, Ahmed FN, Overbey EG, Zoller JA, Mathieu J, Ruohola-Baker H, Ware CB, Hawkins RD. Enhancer chromatin and 3D genome architecture changes from naive to primed human embryonic stem cell states. Stem Cell Reports. 2019;12:1129–1144. doi: 10.1016/j.stemcr.2019.04.004. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bayerl J, Ayyash M, Shani T, Manor YS, Gafni O, Massarwa R, Kalma Y, Aguilera-Castrejon A, Zerbib M, Amir H, Sheban D, Geula S, Mor N, Weinberger L, Naveh Tassa S, Krupalnik V, Oldak B, Livnat N, Tarazi S, Tawil S, Wildschutz E, Ashouokhi S, Lasman L, Rotter V, Hanna S, Ben-Yosef D, Novershtern N, Viukov S, Hanna JH. Principles of signaling pathway modulation for enhancing human naive pluripotency induction. Cell Stem Cell. 2021;S1934-5909:00158-2. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2021.04.001. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

