Behavioral Strategies to Minimize Procedural Distress During In-Office Pediatric Tympanostomy Tube Placement Without Sedation or Restraint
- PMID: 34463896
- PMCID: PMC9184402
- DOI: 10.1007/s10880-021-09813-0
Behavioral Strategies to Minimize Procedural Distress During In-Office Pediatric Tympanostomy Tube Placement Without Sedation or Restraint
Abstract
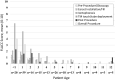
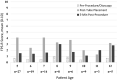
The purpose of this study was to evaluate behavioral strategies to minimize procedural distress associated with in-office tympanostomy tube placement for children without general anesthesia, sedation, or papoose-board restraints. 120 6-month- to 4-year-olds and 102 5- to 12-year-olds were treated at 16 otolaryngology practices. Mean age of children was 4.7 years old (SD = 3.18 years), with more boys (58.1%) than girls (41.9%). The cohort included 14% Hispanic or Latinx, 84.2% White, 12.6% Black, 1.8% Asian and 4.1% 'Other' race and ethnicity classifications. The in-office tube placement procedure included local anesthesia via lidocaine/epinephrine iontophoresis and tube placement using an integrated and automated myringotomy and tube delivery system. Behavioral strategies were used to minimize procedural distress. Anxiolytics, sedation, or papoose board were not used. Pain was measured via the faces pain scale-revised (FPS-R) self-reported by the children ages 5 through 12 years. Independent coders supervised by a psychologist completed the face, legs, activity, cry, consolability (FLACC) behavior observational rating scale to quantify children's distress. Mean FPS-R score for tube placement was 3.30, in the "mild' pain range, and decreased to 1.69 at 5-min post-procedure. Mean tube placement FLACC score was 4.0 (out of a maximum score of 10) for children ages 6 months to 4 years and was 0.4 for children age 5-12 years. Mean FLACC score 3-min post-tube placement was 1.3 for children ages 6 months to 4 years and was 0.2 for children age 5-12 years. FLACC scores were inversely correlated with age, with older children displaying lower distress. The iontophoresis, tube delivery system and behavioral program were associated with generally low behavioral distress. These data suggest that pediatric tympanostomy and tube placement can be achieved in the outpatient setting without anxiolytics, sedatives, or mechanical restraints.
Keywords: Distraction; Myringotomy; Pediatric; Preparation techniques; Procedural distress; Tympanostomy tube placement.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Lindsey L. Cohen, Abigail S. Robbertz, and Laura J. England declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Behavioral techniques to optimize success of in-office pediatric tympanostomy tube placement without sedation.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2015 Dec;79(12):2170-3. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2015.09.041. Epub 2015 Oct 8. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2015. PMID: 26514928 Clinical Trial.
-
In-Office Tympanostomy Tube Placement in Children Using Iontophoresis and Automated Tube Delivery.Laryngoscope. 2020 May;130 Suppl 4(Suppl 4):S1-S9. doi: 10.1002/lary.28612. Epub 2020 Mar 11. Laryngoscope. 2020. PMID: 32160320 Free PMC article.
-
Tympanostomy tube placement in awake, unrestrained pediatric patients: A prospective, multicenter study.Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2015 Dec;79(12):2416-23. doi: 10.1016/j.ijporl.2015.11.003. Epub 2015 Nov 10. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol. 2015. PMID: 26611339 Clinical Trial.
-
Factors Associated With Low Procedural Pain Scores Among 1- to 5-Year-Old Patients Undergoing Facial Laceration Repair.Pediatr Emerg Care. 2023 Mar 1;39(3):135-141. doi: 10.1097/PEC.0000000000002744. Epub 2022 May 17. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2023. PMID: 35608526 Review.
-
In-office Tympanostomy Tube Placement in Children.Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2025 Aug;58(4):613-621. doi: 10.1016/j.otc.2025.03.016. Epub 2025 May 16. Otolaryngol Clin North Am. 2025. PMID: 40382229 Review.
Cited by
-
Feasibility of a Novel Autoinflation Device to Treat Pediatric Otitis Media With Effusion At-Home.OTO Open. 2025 May 14;9(2):e70128. doi: 10.1002/oto2.70128. eCollection 2025 Apr-Jun. OTO Open. 2025. PMID: 40370996 Free PMC article.
-
Invasive procedures and atraumatic care in pediatric nursing practice: nurses' perceptions.Front Pediatr. 2025 May 15;13:1543138. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1543138. eCollection 2025. Front Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 40443573 Free PMC article.
-
The Emerging Role of Virtual Reality as an Adjunct to Procedural Sedation and Anesthesia: A Narrative Review.J Clin Med. 2023 Jan 20;12(3):843. doi: 10.3390/jcm12030843. J Clin Med. 2023. PMID: 36769490 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Asvanund Y, Mitrakul K, Juhong RO, Arunakul M. Effect of audiovisual eyeglasses during local anesthesia injections in 5-to 8-year-old children. Quintessence International. 2015;46:513–521. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous