Amyloid beta acts synergistically as a pro-inflammatory cytokine
- PMID: 34464705
- PMCID: PMC8502211
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nbd.2021.105493
Amyloid beta acts synergistically as a pro-inflammatory cytokine
Abstract
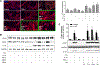
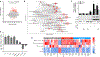
The amyloid beta (Aβ) peptide is believed to play a central role in Alzheimer's disease (AD), the most common age-related neurodegenerative disorder. However, the natural, evolutionarily selected functions of Aβ are incompletely understood. Here, we report that nanomolar concentrations of Aβ act synergistically with known cytokines to promote pro-inflammatory activation in primary human astrocytes (a cell type increasingly implicated in brain aging and AD). Using transcriptomics (RNA-seq), we show that Aβ can directly substitute for the complement component C1q in a cytokine cocktail previously shown to induce astrocyte immune activation. Furthermore, we show that astrocytes synergistically activated by Aβ have a transcriptional signature similar to neurotoxic "A1" astrocytes known to accumulate with age and in AD. Interestingly, we find that this biological action of Aβ at low concentrations is distinct from the transcriptome changes induced by the high/supraphysiological doses of Aβ often used in in vitro studies. Collectively, our results suggest an important, cytokine-like function for Aβ and a novel mechanism by which it may directly contribute to the neuroinflammation associated with brain aging and AD.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; Amyloid beta; Astrocytes; Inflammation; Transcriptomics.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Akiyama H, Kawamata T, Yamada T, Tooyama I, Ishii T, McGeer PL, 1993. Expression of intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1 by a subset of astrocytes in Alzheimer disease and some other degenerative neurological disorders. Acta Neuropathol. 85, 628–634. - PubMed
-
- Bales KR, Du Y, Holtzman D, Cordell B, Paul SM, 2000. Neuroinflammation and Alzheimer’s disease: critical roles for cytokine/Abeta-induced glial activation, NF-kappaB, and apolipoprotein E. Neurobiol. Aging 21, 427–432 (discussion 451–423). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

