Asthmatic allergen inhalation sensitises carotid bodies to lysophosphatidic acid
- PMID: 34465362
- PMCID: PMC8408927
- DOI: 10.1186/s12974-021-02241-9
Asthmatic allergen inhalation sensitises carotid bodies to lysophosphatidic acid
Abstract
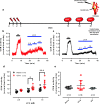
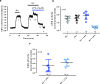
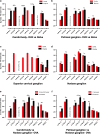
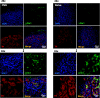
The carotid bodies are multimodal sensors that regulate various autonomic reflexes. Recent evidence demonstrates their role in immune reflex regulation. Our previous studies using the allergen (ovalbumin) sensitised and exposed Brown Norway rat model of asthma suggest that carotid bodies mediate asthmatic bronchoconstriction through a lysophosphatidic acid (LPA) receptor (LPAr)-protein kinase C epsilon (PKCε)-transient receptor potential vanilloid one channel (TRPV1) pathway. Whilst naïve carotid bodies respond to LPA, whether their response to LPA is enhanced in asthma is unknown. Here, we show that asthmatic sensitisation of Brown Norway rats involving repeated aerosolised allergen challenges over 6 days, results in an augmentation of the carotid bodies' acute sensitivity to LPA. Increased expression of LPAr in the carotid bodies and petrosal ganglia likely contributed to this sensitivity. Importantly, allergen sensitisation of the carotid bodies to LPA did not alter their hypoxic response, nor did hypoxia augment LPA sensitivity acutely. Our data demonstrate the ability of allergens to sensitise the carotid bodies, highlighting the likely role of the carotid bodies and blood-borne inflammatory mediators in asthma.
Keywords: Allergen; Asthma; Carotid body; Lysophosphatidic acid; Neuro-immune; Neuroimmunology; Petrosal ganglion; TRPV1.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
N.G.J., A.R. and R.J.A.W declare the following competing interests. U.S. Patent Application No. 62/534,638, Status: provisional patent; “Method to Abate Acute Airway Hypersensitivity and Asthma Attacks.” Purpose: for the use of TRPV1 and LPAr blockade as a treatment for respiratory distress associated with acute asthmatic attack. Authors are also founders and/or shareholders of AazeinTx Inc., a clinical-stage University spinoff company investigating the use of a TRPV1 antagonist in asthma.
Figures
References
-
- Falvey A, Duprat F, Simon T, Hugues-Ascery S, Conde SV, Glaichenhaus N, Blancou P. Electrostimulation of the carotid sinus nerve in mice attenuates inflammation via glucocorticoid receptor on myeloid immune cells. J Neuroinflammation. 2020;17(1):368. doi: 10.1186/s12974-020-02016-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nardocci G, Martin A, Abarzúa S, Rodríguez J, Simon F, Reyes EP, Acuña-Castillo C, Navarro C, Cortes PP, Fernández R. Sepsis progression to multiple organ dysfunction in carotid chemo/baro-denervated rats treated with lipopolysaccharide. J Neuroimmunol. 2015;278:44–52. doi: 10.1016/j.jneuroim.2014.12.002. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

