Ivermectin: a multifaceted drug of Nobel prize-honoured distinction with indicated efficacy against a new global scourge, COVID-19
- PMID: 34466270
- PMCID: PMC8383101
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nmni.2021.100924
Ivermectin: a multifaceted drug of Nobel prize-honoured distinction with indicated efficacy against a new global scourge, COVID-19
Abstract
In 2015, the Nobel Committee for Physiology or Medicine, in its only award for treatments of infectious diseases since six decades prior, honoured the discovery of ivermectin (IVM), a multifaceted drug deployed against some of the world's most devastating tropical diseases. Since March 2020, when IVM was first used against a new global scourge, COVID-19, more than 20 randomized clinical trials (RCTs) have tracked such inpatient and outpatient treatments. Six of seven meta-analyses of IVM treatment RCTs reporting in 2021 found notable reductions in COVID-19 fatalities, with a mean 31% relative risk of mortality vs. controls. During mass IVM treatments in Peru, excess deaths fell by a mean of 74% over 30 days in its ten states with the most extensive treatments. Reductions in deaths correlated with the extent of IVM distributions in all 25 states with p < 0.002. Sharp reductions in morbidity using IVM were also observed in two animal models, of SARS-CoV-2 and a related betacoronavirus. The indicated biological mechanism of IVM, competitive binding with SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, is likely non-epitope specific, possibly yielding full efficacy against emerging viral mutant strains.
Keywords: COVID-19; H. pylori; SARS-CoV-2; ivermectin; spike protein.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Figures
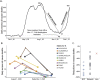
 ), mean -74%; moderate-local distributions (
), mean -74%; moderate-local distributions ( ), mean -53%; and minimal-Lima (
), mean -53%; and minimal-Lima ( ), -25%. The absolute value of these reductions by state correlated with extent of IVM distributions with Kendall τb = 0.524, p < 0.002 (Spearman rho = 0.619, p < 0.001). All these data are from publicly accessible Peruvian national databases, with associated frozen datasets available from the Dryad data repository [42].
), -25%. The absolute value of these reductions by state correlated with extent of IVM distributions with Kendall τb = 0.524, p < 0.002 (Spearman rho = 0.619, p < 0.001). All these data are from publicly accessible Peruvian national databases, with associated frozen datasets available from the Dryad data repository [42].References
-
- Ergonul O., Yalcin C.E., Erkent M.A., Demirci M., Uysal S.P., Ay N.Z. Who can get the next Nobel Prize in infectious diseases? Int J Infect Dis. 2016;45:88–91. - PubMed
-
- Yagisawa M., Foster P.J., Hanaki H., Omura S. Global trends in clinical studies of ivermectin in COVID-19. Japanes J Antib. 2021;74(1)
-
- Campbell W.C. History of avermectin and ivermectin, with notes on the history of other macrocyclic lactone antiparasitic agents. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2012;13(6):853–865. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
