Effect of nutrition counselling with a digital job aid on child dietary diversity: Analysis of secondary outcomes from a cluster randomised controlled trial in rural Bangladesh
- PMID: 34467669
- PMCID: PMC8710107
- DOI: 10.1111/mcn.13267
Effect of nutrition counselling with a digital job aid on child dietary diversity: Analysis of secondary outcomes from a cluster randomised controlled trial in rural Bangladesh
Abstract
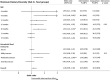
Adequate dietary diversity among infants is often suboptimal in developing countries. We assessed the impact of nutrition counselling using a digital job aid on dietary diversity of children aged 6-23 months using data from a cluster randomised controlled trial in Bangladesh. The trial had five arms, each with 25 clusters. The four intervention arms provided counselling using a digital job aid and different prenatal and post-natal combinations of lipid-based supplements and the comparison arm with usual practice. We enrolled 1500 pregnant women and followed them until the children reached their second birthday. We developed a tablet-based system for intervention delivery, data collection and project supervision. We combined the four intervention arms (n = 855), in which community health workers (CHWs) provided age-appropriate complementary feeding counselling, to compare against the comparison arm (n = 403). We calculated the outcome indicators from the children's 24-h dietary recalls. Overall, the intervention increased the mean dietary diversity score by 0.09 (95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.2-0.16) and odds of minimum dietary diversity by 18% (95% CI: 0.99-1.40). However, there was a significant interaction on the effect of the intervention on dietary diversity by age. The mean dietary diversity score was 0.24 (95% CI: 0.11-0.37) higher in the intervention than in the comparison arm at 9 months and 0.14 (95% CI: 0.01-27) at 12 months of age. The intervention effect was non-significant at an older age. Overall, consumption of flesh food was 1.32 times higher in the intervention arm (odds ratio [OR] 1.32, 95% CI: 1.11-1.57) in 6-23 months of age. The intervention significantly improved child dietary diversity score in households with mild and moderate food insecurity by 0.27 (95% CI: 0.06-0.49) and 0.16 (0.05-27), respectively, but not with food-secure and severely food-insecure households. Although the study did not evaluate the impact of digital job aid alone, the findings indicate the utility of nutrition counselling by CHWs using a digital job aid to improve child feeding practices in broader programmes.
Keywords: cluster randomised controlled trial; community based; counselling; dietary patterns; infant feeding; mHealth; nutrition education.
© 2021 International Centre for Diarrhoeal Disease Reseach, Bangladesh (icddr,b). Maternal & Child Nutrition published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ahmed, A. U. , Hoddinott, J. F. , Roy, S. , Sraboni, E. , Quabili, W. R. , & Margolies, A. (2016). Which kinds of social safety net transfers work best for the ultra poor in Bangladesh?: Operation and impacts of the transfer modality research initiative. Retrieved from Dhaka.
-
- Ara, G. , Khanam, M. , Papri, N. , Nahar, B. , Kabir, I. , Sanin, K. I. , Khan, S. S. , Sarker, M. S. A. , & Dibley, M. J. (2019). Peer counseling promotes appropriate infant feeding practices and improves infant growth and development in an urban slum in Bangladesh: A community‐based cluster randomized controlled trial. Current Developments in Nutrition, 3(7), nzz072. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Arimond, M. , Abbeddou, S. , Kumwenda, C. , Okronipa, H. , Hemsworth, J. , Jimenez, E. Y. , Ocansey, E. , Lartey, A. , Ashorn, U. , Adu‐Afarwuah, S. , Vosti, S. A. , Hess, S. Y. , & Dewey, K. G. (2017). Impact of small quantity lipid‐based nutrient supplements on infant and young child feeding practices at 18 months of age: Results from four randomized controlled trials in Africa. Maternal & Child Nutrition, 13(3), e12377. 10.1111/mcn.12377 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bhandari, N. , Mazumder, S. , Bahl, R. , Martines, J. , Black, R. E. , Bhan, M. K. , & Infant Feeding Study Group . (2004). An educational intervention to promote appropriate complementary feeding practices and physical growth in infants and young children in rural Haryana, India. The Journal of Nutrition, 134(9), 2342–2348. 10.1093/jn/134.9.2342 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

