Antigen Test Performance Among Children and Adults at a SARS-CoV-2 Community Testing Site
- PMID: 34468732
- PMCID: PMC8932441
- DOI: 10.1093/jpids/piab081
Antigen Test Performance Among Children and Adults at a SARS-CoV-2 Community Testing Site
Abstract
Background: Performance characteristics of SARS-CoV-2 antigen tests among children are limited despite the need for point-of-care testing in school and childcare settings. We describe children seeking SARS-CoV-2 testing at a community site and compare antigen test performance to real-time reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) and viral culture.
Methods: Two anterior nasal specimens were self-collected for BinaxNOW antigen and RT-PCR testing, along with demographics, symptoms, and exposure information from individuals ≥5 years at a community testing site. Viral culture was attempted on residual antigen or RT-PCR-positive specimens. Demographic and clinical characteristics, and the performance of SARS-CoV-2 antigen tests, were compared among children (<18 years) and adults.
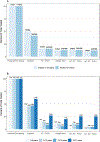
Results: About 1 in 10 included specimens were from children (225/2110); 16.4% (37/225) were RT-PCR-positive. Cycle threshold values were similar among RT-PCR-positive specimens from children and adults (22.5 vs 21.3, P = .46) and among specimens from symptomatic and asymptomatic children (22.5 vs 23.2, P = .39). Sensitivity of antigen test compared to RT-PCR was 73.0% (27/37) among specimens from children and 80.8% (240/297) among specimens from adults; among specimens from children, specificity was 100% (188/188), positive and negative predictive values were 100% (27/27) and 94.9% (188/198), respectively. Virus was isolated from 51.4% (19/37) of RT-PCR-positive pediatric specimens; all 19 had positive antigen test results.
Conclusions: With lower sensitivity relative to RT-PCR, antigen tests may not diagnose all positive COVID-19 cases; however, antigen testing identified children with live SARS-CoV-2 virus.
Keywords: COVID-19; epidemiology; infectious diseases; pediatrics; public health.
Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of The Journal of the Pediatric Infectious Diseases Society 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Jenco M. COVID-19 Cases in Children Surpass 2 Million. Itasca, IL: AAP News: American Academy of Pediatrics; 2020. https://www.aappublications.org/news/2020/12/29/covid-2million-children-...
-
- Laws RL, Chancey RJ, Rabold EM, et al. Symptoms and transmission of SARS-CoV-2 among children — Utah and Wisconsin, March–May 2020. Pedriatrics 2021; 147(1):e2020027268. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

