Hospital transfusion service operations during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic: Lessons learned from the AABB hospital survey in preparation for the next infectious disease outbreak
- PMID: 34469010
- PMCID: PMC8661942
- DOI: 10.1111/trf.16643
Hospital transfusion service operations during the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic: Lessons learned from the AABB hospital survey in preparation for the next infectious disease outbreak
Abstract
Background: The SARS-CoV-2 pandemic disrupted hospital operations, affected the blood supply, and challenged the health care system to develop new therapeutic options, including convalescent plasma (CCP). The aim of this study is to describe and analyze blood supply fluctuations and the use of convalescent plasma in 2020.
Methods: AABB distributed a weekly and biweekly questionnaire through email to hospital-based members (HBM).
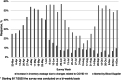
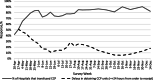
Results: The survey was sent to 887 HBM with 479 unique respondents, most of the hospitals served pediatric and adult patients, and all states of the country participated, except Idaho and Vermont. Fifty four percent of HBM reported increased wastage in the early phase of the pandemic (May), which decreased to 4% by the end of June and throughout the rest of the year. The majority of HBM reported receiving alerts from their blood suppliers reporting blood shortages throughout the year. During March and April, only 12% of HBM were performing elective surgical procedures. The top reasons to delay procedures were: bed availability (28%); COVID-19 caseload (23%; and blood availability (19%). By mid-April, 42% HBM had transfused CCP and reported >24 h delay in getting the units; the vast majority obtained CCP using the Expanded Access Protocol, and later, the Emergency Use Authorization. HBM consistently prioritized the most severe patients to receive CCP, but the proportion of severely ill recipients fell from 52% to 37% between May and October, with an increase from 5% to 21% of HBM providing CCP transfusion early in the course of the disease.
Discussion: Blood utilization and availability fluctuated during the pandemic. The fluctuations appeared to be related to the number of COVID-19 in the community. The use and regulatory landscape of CCP rapidly evolved over the first 8 months of the pandemic.
Keywords: blood supply; blood transfusions; hospital operations; pandemic; transfusion services.
© 2021 AABB.
Conflict of interest statement
Nothing to disclose.
Figures


References
-
- World Health Organization . Listings of WHO's response to COVID‐19. 2020 [cited 2021 Aug 1]. Available from: https://www.who.int/news/item/29-06-2020-covidtimeline.
-
- Pagano MB, Hess JR, Tsang HC, Staley E, Gernsheimer T, Sen N, et al. Prepare to adapt: blood supply and transfusion support during the first 2 weeks of the 2019 novel coronavirus (COVID‐19) pandemic affecting Washington State. Transfusion. 2020;60(5):908–11. - PubMed
-
- World Health Organization . Maintaining a safe and adequate blood supply during the pandemic outbreak of coronavirus disease (COVID‐19): interim guidance. Geneva PP—Geneva: World Health Organization; 2020. Available from: https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/331523
-
- AABB, America's Blood Centers, American Red Cross . Joint statement on the nation's blood supply. 2020. [cited 2021 Aug 3]. Available from: https://www.redcross.org/about-us/news-and-events/press-release/2020/joi....
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

