Machine learning gene expression predicting model for ustekinumab response in patients with Crohn's disease
- PMID: 34469062
- PMCID: PMC8589399
- DOI: 10.1002/iid3.506
Machine learning gene expression predicting model for ustekinumab response in patients with Crohn's disease
Abstract
Background: Recent studies reported the responses of ustekinumab (UST) for the treatment of Crohn's disease (CD) differ among patients, while the cause was unrevealed. The study aimed to develop a prediction model based on the gene transcription profiling of patients with CD in response to UST.
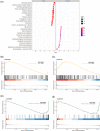
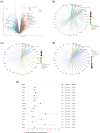
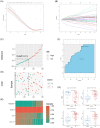
Methods: The GSE112366 dataset, which contains 86 CD and 26 normal samples, was downloaded for analysis. Differentially expressed genes (DEGs) were identified first. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) pathway analyses were administered. Least absolute shrinkage and selection operator regression analysis was performed to build a model for UST response prediction.
Results: A total of 122 DEGs were identified. GO and KEGG analyses revealed that immune response pathways are significantly enriched in patients with CD. A multivariate logistic regression equation that comprises four genes (HSD3B1, MUC4, CF1, and CCL11) for UST response prediction was built. The area under the receiver operator characteristic curve for patients in training set and testing set were 0.746 and 0.734, respectively.
Conclusions: This study is the first to build a gene expression prediction model for UST response in patients with CD and provides valuable data sources for further studies.
Keywords: Crohn's disease; LASSO regression; machine learning model; ustekinumab.
© 2021 The Authors. Immunity, Inflammation and Disease published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests.
Figures
References
-
- Kaplan GG. The global burden of IBD: from 2015 to 2025. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2015;12(12):720‐727. - PubMed
-
- Feagan BG, Sandborn WJ, Gasink C, et al. Ustekinumab as induction and maintenance therapy for Crohn's disease. N Engl J Med. 2016;375(20):1946‐1960. - PubMed
-
- Geremia A, Satsangi J. The role of genetics in Crohn's disease: how could it influence future therapies? Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018;12(11):1075‐1077. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

