MiR-212-3p promotes proliferation and migration of trophoblast in fetal growth restriction by targeting placental growth factor
- PMID: 34470571
- PMCID: PMC8806470
- DOI: 10.1080/21655979.2021.1967069
MiR-212-3p promotes proliferation and migration of trophoblast in fetal growth restriction by targeting placental growth factor
Abstract
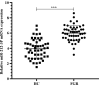
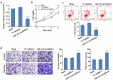
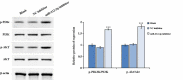
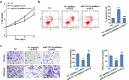
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the function and possible mechanism of miR-212-3p in fetal growth restriction (FGR) and to demonstrate the relationship between miR-212-3p and placental growth factor (PGF). First, we used qRT-PCR to detect the expression of miR-212-3p and PGF in placental tissues of normal delivery (HC group) and FGR, as well as in human trophoblast cell HTR-8/Svneo. The results revealed that miR-212-3p expression was significantly upregulated and PGF was significantly downregulated in placental tissue in the FGR group compared with the HC group. In addition, interference with miR-212-3p expression increased the proliferation, invasion, and migration of HTR-8/SVneo cells and decreased apoptosis of cells. Meanwhile, Western blot results showed that miR-212-3p expression downregulation promoted the phosphorylated protein expression of Phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K) and protein kinase B (AKT), which in turn activated the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. And the results of dual luciferase reporter further showed that miR-212-3p could target PGF, and the expression of both was negatively correlated in FGR group tissues. In addition, downregulation of miR-212-3p expression reversed the inhibitory effect of PGF downregulation on HTR-8/SVneo cells. In conclusion, miR-212-3p can target and inhibit the PGF expression and regulate the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway to regulate trophoblast cell invasion, migration, proliferation and cell apoptosis. This provides a potential biomarker for the development of FGR.
Keywords: Fetal growth restriction; PGF; PI3K/AKT signaling pathway; biomarkers; miR-212-3p.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
Figures

References
-
- Stanek J. Hypoxic patterns of placental injury: a review. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2013;137:706–720. - PubMed
-
- Fujimaki A, Watanabe K, Mori T, et al. Placental oxidative DNA damage and its repair in preeclamptic women with fetal growth restriction. Placenta. 2011;32:367–372. - PubMed
-
- American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists. ACOG Practice Bulletin No. 204: fetal growth restriction. Obstetrics and gynecology, 2019;133:e97–e109. - PubMed
-
- Juan Q, Hongbo Q.. Fetal growth restriction: an updated understanding. Chin J Perinat Med. 2015;18:418–420.
-
- Sharma D, Farahbakhsh N, Shastri S, et al. Intrauterine growth restriction - part 2. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2016;29:4037–4048. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
