Aging, inflammation and DNA damage in the somatic testicular niche with idiopathic germ cell aplasia
- PMID: 34471128
- PMCID: PMC8410861
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-021-25544-0
Aging, inflammation and DNA damage in the somatic testicular niche with idiopathic germ cell aplasia
Abstract
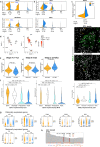
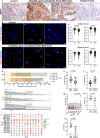
Molecular mechanisms associated with human germ cell aplasia in infertile men remain undefined. Here we perform single-cell transcriptome profiling to highlight differentially expressed genes and pathways in each somatic cell type in testes of men with idiopathic germ cell aplasia. We identify immaturity of Leydig cells, chronic tissue inflammation, fibrosis, and senescence phenotype of the somatic cells, as well markers of chronic inflammation in the blood. We find that deregulated expression of parentally imprinted genes in myoid and immature Leydig cells, with relevant changes in the ratio of Lamin A/C transcripts and an active DNA damage response in Leydig and peritubular myoid cells are also indicative of senescence of the testicular niche. This study offers molecular insights into the pathogenesis of idiopathic germ cell aplasia.
© 2021. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures




Comment in
-
Understanding iGCA.Nat Rev Urol. 2021 Nov;18(11):638. doi: 10.1038/s41585-021-00531-8. Nat Rev Urol. 2021. PMID: 34625738 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

