TS-m6A-DL: Tissue-specific identification of N6-methyladenosine sites using a universal deep learning model
- PMID: 34471503
- PMCID: PMC8383060
- DOI: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.08.014
TS-m6A-DL: Tissue-specific identification of N6-methyladenosine sites using a universal deep learning model
Abstract
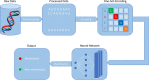
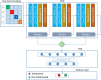
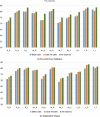
The most communal post-transcriptional modification, N6-methyladenosine (m6A), is associated with a number of crucial biological processes. The precise detection of m6A sites around the genome is critical for revealing its regulatory function and providing new insights into drug design. Although both experimental and computational models for detecting m6A sites have been introduced, but these conventional methods are laborious and expensive. Furthermore, only a handful of these models are capable of detecting m6A sites in various tissues. Therefore, a more generic and optimized computational method for detecting m6A sites in different tissues is required. In this paper, we proposed a universal model using a deep neural network (DNN) and named it TS-m6A-DL, which can classify m6A sites in several tissues of humans (Homo sapiens), mice (Mus musculus), and rats (Rattus norvegicus). To extract RNA sequence features and to convert the input into numerical format for the network, we utilized one-hot-encoding method. The model was tested using fivefold cross-validation and its stability was measured using independent datasets. The proposed model, TS-m6A-DL, achieved accuracies in the range of 75-85% using the fivefold cross-validation method and 72-84% on the independent datasets. Finally, to authenticate the generalization of the model, we performed cross-species testing and proved the generalization ability by achieving state-of-the-art results.
Keywords: Binary-encoding; Deep neural network; Motif; N6-methyladenosine (m6A); Tissue-specific.
© 2021 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures


Similar articles
-
DNN-m6A: A Cross-Species Method for Identifying RNA N6-Methyladenosine Sites Based on Deep Neural Network with Multi-Information Fusion.Genes (Basel). 2021 Feb 28;12(3):354. doi: 10.3390/genes12030354. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33670877 Free PMC article.
-
ELMo4m6A: A Contextual Language Embedding-Based Predictor for Detecting RNA N6-Methyladenosine Sites.IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2023 Mar-Apr;20(2):944-954. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2022.3173323. Epub 2023 Apr 3. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 35536814
-
DL-m6A: Identification of N6-Methyladenosine Sites in Mammals Using Deep Learning Based on Different Encoding Schemes.IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2023 Mar-Apr;20(2):904-911. doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2022.3192572. Epub 2023 Apr 3. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinform. 2023. PMID: 35857733
-
Comprehensive review and assessment of computational methods for predicting RNA post-transcriptional modification sites from RNA sequences.Brief Bioinform. 2020 Sep 25;21(5):1676-1696. doi: 10.1093/bib/bbz112. Brief Bioinform. 2020. PMID: 31714956 Review.
-
Predicting N6-Methyladenosine Sites in Multiple Tissues of Mammals through Ensemble Deep Learning.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Dec 7;23(24):15490. doi: 10.3390/ijms232415490. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36555143 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
CNNLSTMac4CPred: A Hybrid Model for N4-Acetylcytidine Prediction.Interdiscip Sci. 2022 Jun;14(2):439-451. doi: 10.1007/s12539-021-00500-0. Epub 2022 Feb 1. Interdiscip Sci. 2022. PMID: 35106702
-
Optimizing Hyperparameter Tuning in Machine Learning to Improve the Predictive Performance of Cross-Species N6-Methyladenosine Sites.ACS Omega. 2023 Oct 13;8(42):39420-39426. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.3c05074. eCollection 2023 Oct 24. ACS Omega. 2023. PMID: 37901522 Free PMC article.
-
Crosstalk between m6A and coding/non-coding RNA in cancer and detection methods of m6A modification residues.Aging (Albany NY). 2023 Jul 11;15(13):6577-6619. doi: 10.18632/aging.204836. Epub 2023 Jul 11. Aging (Albany NY). 2023. PMID: 37437245 Free PMC article. Review.
-
m6A-TSHub: Unveiling the Context-specific m6A Methylation and m6A-affecting Mutations in 23 Human Tissues.Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2023 Aug;21(4):678-694. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2022.09.001. Epub 2022 Sep 9. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2023. PMID: 36096444 Free PMC article.
-
Dynamic regulation and key roles of ribonucleic acid methylation.Front Cell Neurosci. 2022 Dec 19;16:1058083. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2022.1058083. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Neurosci. 2022. PMID: 36601431 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Sun Xi Hong, Zhao Ling Ping, Zou Quan, Wang Zhan Bin. Identification of microrna genes and their mrna targets in festuca arundinacea. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2014;172(8):3875–3887. - PubMed
-
- Toone Eric J. Advances in enzymology and related areas of molecular biology, volume 240. John Wiley & Sons. 2011 - PubMed
-
- Bokar Joseph A. Springer; 2005. The biosynthesis and functional roles of methylated nucleosides in eukaryotic mrna. In Fine-tuning of RNA functions by modification and editing; pp. 141–177.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
