Revisiting the Balz-Schiemann Reaction of Aryldiazonium Tetrafluoroborate in Different Solvents under Catalyst- and Additive-Free Conditions
- PMID: 34471763
- PMCID: PMC8388107
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.1c02825
Revisiting the Balz-Schiemann Reaction of Aryldiazonium Tetrafluoroborate in Different Solvents under Catalyst- and Additive-Free Conditions
Abstract
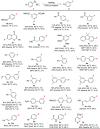
The thermal and photochemical Balz-Schiemann reaction in commonly used solvents was revisited under catalyst- and additive-free conditions. The study showed that using low- or non-polar solvents could improve the pyrolysis and photolysis of aryldiazonium tetrafluoroborates, enabling effective fluorination at a low temperature or under visible-light irradiation. PhCl and hexane were exemplified as cheap and reliable solvents for both reactions, providing good to excellent yields of aryl fluorides from the corresponding diazonium tetrafluoroborates. The combination of slight heating with visible-light irradiation was beneficial for the transformation of stable aryldiazonium tetrafluoroborates. Nevertheless, the electronic and steric nature of aryldiazonium tetrafluoroborates still had a pivotal effect on both fluorinations even in these solvents.
© 2021 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures

References
-
- Kirsch P.Modern Fluoroorganic Chemistry, 2nd ed.; Wiley-VCH, 2013.
-
- Lowe P. T.; O’Hagan D. A role for fluorine in flavours, fragrances and pheromones. J. Fluorine Chem. 2020, 230, 10942010.1016/j.jfluchem.2019.109420. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

