Mitochondrial dysfunctions in neurodegenerative diseases: role in disease pathogenesis, strategies for analysis and therapeutic prospects
- PMID: 34472461
- PMCID: PMC8530118
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.322430
Mitochondrial dysfunctions in neurodegenerative diseases: role in disease pathogenesis, strategies for analysis and therapeutic prospects
Abstract
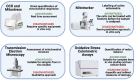
Fundamental organelles that occur in every cell type with the exception of mammal erythrocytes, the mitochondria are required for multiple pivotal processes that include the production of biological energy, the biosynthesis of reactive oxygen species, the control of calcium homeostasis, and the triggering of cell death. The disruption of anyone of these processes has been shown to impact strongly the function of all cells, but especially of neurons. In this review, we discuss the role of the mitochondria impairment in the development of the neurodegenerative diseases Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis, Parkinson's disease and Alzheimer's disease. We highlight how mitochondria disruption revolves around the processes that underlie the mitochondria's life cycle: fusion, fission, production of reactive oxygen species and energy failure. Both genetic and sporadic forms of neurodegenerative diseases are unavoidably accompanied with and often caused by the dysfunction in one or more of the key mitochondrial processes. Therefore, in order to get in depth insights into their health status in neurodegenerative diseases, we need to focus into innovative strategies aimed at characterizing the various mitochondrial processes. Current techniques include Mitostress, Mitotracker, transmission electron microscopy, oxidative stress assays along with expression measurement of the proteins that maintain the mitochondrial health. We will also discuss a panel of approaches aimed at mitigating the mitochondrial dysfunction. These include canonical drugs, natural compounds, supplements, lifestyle interventions and innovative approaches as mitochondria transplantation and gene therapy. In conclusion, because mitochondria are fundamental organelles necessary for virtually all the cell functions and are severely impaired in neurodegenerative diseases, it is critical to develop novel methods to measure the mitochondrial state, and novel therapeutic strategies aimed at improving their health.
Keywords: Alzheimer’s disease; Mitostress; Mitotracker; Parkinson’s disease; amyotrophic lateral sclerosis; mitochondria; mitochondria modulation; mitochondrial dysfunction; mitochondrial health; neurodegenerative disease.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures

References
-
- Burté F, Carelli V, Chinnery PF, Yu-Wai-Man P. Disturbed mitochondrial dynamics and neurodegenerative disorders. Nat Rev Neurol. 2015;11:11–24. - PubMed
-
- Cottet-Rousselle C, Ronot X, Leverve X, Mayol JF. Cytometric assessment of mitochondria using fluorescent probes. Cytometry A. 2011;79:405–425. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

