Xenon as a transdermal enhancer for niacinamide in Strat-M™ membranes
- PMID: 34472499
- PMCID: PMC8447954
- DOI: 10.4103/2045-9912.320704
Xenon as a transdermal enhancer for niacinamide in Strat-M™ membranes
Abstract
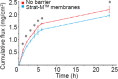
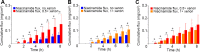
Xenon is confirmed to diffuse readily through membranes and has properties of transdermal enhancer. In this study, the ability of xenon to regulate the transdermal diffusion of niacinamide was investigated using a model of an artificial skin analogue of Strat-M™ membranes in Franz cells. Based on the data obtained, we found that in the simplified biophysical model of Strat-M™ membranes xenon exerts its enhancer effect based on the heterogeneous nucleation of xenon at the interfaces in the microporous structures of Strat-M™ membranes.
Keywords: Franz cell; Strat-M; enhancer; gas nucleation; niacinamide; permeation; skin; transdermal drug delivery system; xenon.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures


References
-
- Prangé T, Schiltz M, Pernot L, et al. Exploring hydrophobic sites in proteins with xenon or krypton. Proteins. 1998;30:61–73. - PubMed
-
- Booker RD, Sum AK. Biophysical changes induced by xenon on phospholipid bilayers. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1828:1347–1356. - PubMed
-
- Reyes-Figueroa AD, Karttunen M, Ruiz-Suárez JC. Cholesterol sequestration by xenon nano bubbles leads to lipid raft destabilization. Soft Matter. 2020;16:9655–9661. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

