Virus-specific T cells for adenovirus infection after stem cell transplantation are highly effective and class II HLA restricted
- PMID: 34473237
- PMCID: PMC8525242
- DOI: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2021004456
Virus-specific T cells for adenovirus infection after stem cell transplantation are highly effective and class II HLA restricted
Abstract
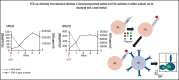
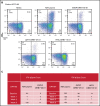
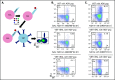
Infection with adenoviruses is a common and significant complication in pediatric patients after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Treatment options with traditional antivirals are limited by poor efficacy and significant toxicities. T-cell reconstitution is critical for the management of adenoviral infections, but it generally takes place months after transplantation. Ex vivo-generated virus-specific T cells (VSTs) are an alternative approach for viral control and can be rapidly generated from either a stem cell donor or a healthy third-party donor. In the context of a single-center phase 1/2 clinical trial, we treated 30 patients with a total of 43 infusions of VSTs for adenoviremia and/or adenoviral disease. Seven patients received donor-derived VSTs, 21 patients received third-party VSTs, and 2 received VSTs from both donor sources. Clinical responses were observed in 81% of patients, with a complete response in 58%. Epitope prediction and potential epitope identification for common HLA molecules helped elucidate HLA restriction in a subset of patients receiving third-party products. Intracellular interferon-γ expression in T cells in response to single peptides and response to cell lines stably transfected with a single HLA molecule demonstrated HLA-restricted CD4+ T-cell response, and these results correlated with clinical outcomes. Taken together, these data suggest that VSTs are a highly safe and effective therapy for the management of adenoviral infection in immunocompromised hosts. The trials were registered at www.clinicaltrials.gov as #NCT02048332 and #NCT02532452.
© 2021 by The American Society of Hematology.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict-of-interest disclosure: C.M.B. is on the advisory board for Cellectis, is on the scientific advisory boards for Catamaran Bio and Mana Therapeutics with stock/or ownership, is on the board of directors for Caballeta Bio with stock options, and has stock in Neximmune and Torque Therapeutics. P.J.H. is a cofounder of and on the board of directors for Mana Therapeutics, on the scientific advisory board of Cellevolve, and has intellectual property related to virus-specific T cells. S.M.D. has a US patent application under review, received research support from Alexion Pharmaceuticals, and served as a consultant for Novartis (unrelated to this work). S.J. has a US patent application under review and received travel support and consultancy fees from Omeros (unrelated to this work). The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures


References
-
- Sahin U, Toprak SK, Atilla PA, Atilla E, Demirer T.. An overview of infectious complications after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. J Infect Chemother. 2016;22(8):505-514. - PubMed
-
- Ali S, Krueger J, Richardson SE, et al. . The yield of monitoring adenovirus in pediatric hematopoietic stem cell transplant patients. Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2019;36(3):161-172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

