Adalimumab and Infliximab Impair SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Responses: Results from a Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Study in 11 422 Biologic-Treated Patients
- PMID: 34473254
- PMCID: PMC8499950
- DOI: 10.1093/ecco-jcc/jjab153
Adalimumab and Infliximab Impair SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Responses: Results from a Therapeutic Drug Monitoring Study in 11 422 Biologic-Treated Patients
Abstract
Background and aims: Infliximab attenuates serological responses to SARS-CoV-2 infection. Whether this is a class effect, or if anti-tumour necrosis factor [anti-TNF] level influences serological responses, remains unknown.
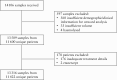
Methods: Seroprevalence and the magnitude of SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid antibody responses were measured in surplus serum from 11 422 (53.3% [6084] male; median age 36.8 years) patients with immune-mediated inflammatory diseases, stored at six therapeutic drug monitoring laboratories between January 29 and September 30, 2020. Data were linked to nationally held SARS-CoV-2 PCR results to July 11, 2021.
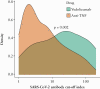
Results: Rates of PCR-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 infection were similar across treatment groups. Seroprevalence rates were lower in infliximab- and adalimumab- than vedolizumab-treated patients (infliximab: 3.0% [178/5893], adalimumab: 3.0% [152/5074], vedolizumab: 6.7% [25/375], p = 0.003). The magnitude of SARS-CoV-2 reactivity was similar in infliximab- vs adalimumab-treated patients (median 4.30 cut-off index [COI] [1.94-9.96] vs 5.02 [2.18-18.70], p = 0.164), but higher in vedolizumab-treated patients (median 21.60 COI [4.39-68.10, p < 0.004). Compared to patients with detectable infliximab and adalimumab drug levels, patients with undetectable drug levels [<0.8 mg/L] were more likely to be seropositive for SARS-CoV-2 antibodies. One-third of patients who had PCR testing prior to antibody testing failed to seroconvert, all were treated with anti-TNF. Subsequent positive PCR-confirmed SARS-CoV-2 was seen in 7.9% [12/152] of patients after a median time of 183.5 days [129.8-235.3], without differences between drugs.
Conclusion: Anti-TNF treatment is associated with lower SARS-CoV-2 nucleocapsid seroprevalence and antibody reactivity when compared to vedolizumab-treated patients. Higher seropositivity rates in patients with undetectable anti-TNF levels support a causal relationship, although confounding factors, such as combination therapy with a immunomodulator, may have influenced the results.
Keywords: CLARITY; COVID-19; adalimumab; biologic; immunosuppression; inflammatory bowel disease; infliximab; vaccination; vedolizumab.
© The Author(s) 2021. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation.
Figures

References
-
- Melmed GY, Agarwal N, Frenck RW, et al. Immunosuppression impairs response to pneumococcal polysaccharide vaccination in patients with inflammatory bowel disease. Am J Gastroenterol 2010;105:148–54. - PubMed
-
- Caldera F, Hillman L, Saha S, et al. Immunogenicity of high dose influenza vaccine for patients with inflammatory bowel disease on anti-TNF monotherapy: a randomized clinical trial. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2020;26:593–602. - PubMed
-
- Elkayam O, Bashkin A, Mandelboim M, et al. The effect of infliximab and timing of vaccination on the humoral response to influenza vaccination in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and ankylosing spondylitis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 2010;39:442–7. - PubMed
-
- Pratt PK Jr, David N, Weber HC, et al. Antibody response to hepatitis B virus vaccine is impaired in patients with inflammatory bowel disease on infliximab therapy. Inflamm Bowel Dis 2018;24:380–6. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

