Tissue environment, not ontogeny, defines murine intestinal intraepithelial T lymphocytes
- PMID: 34473623
- PMCID: PMC8463072
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.70055
Tissue environment, not ontogeny, defines murine intestinal intraepithelial T lymphocytes
Abstract
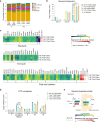
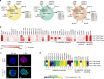
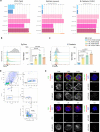
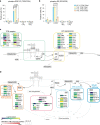
Tissue-resident intestinal intraepithelial T lymphocytes (T-IEL) patrol the gut and have important roles in regulating intestinal homeostasis. T-IEL include both induced T-IEL, derived from systemic antigen-experienced lymphocytes, and natural T-IEL, which are developmentally targeted to the intestine. While the processes driving T-IEL development have been elucidated, the precise roles of the different subsets and the processes driving activation and regulation of these cells remain unclear. To gain functional insights into these enigmatic cells, we used high-resolution, quantitative mass spectrometry to compare the proteomes of induced T-IEL and natural T-IEL subsets, with naive CD8+ T cells from lymph nodes. This data exposes the dominant effect of the gut environment over ontogeny on T-IEL phenotypes. Analyses of protein copy numbers of >7000 proteins in T-IEL reveal skewing of the cell surface repertoire towards epithelial interactions and checkpoint receptors; strong suppression of the metabolic machinery indicating a high energy barrier to functional activation; upregulated cholesterol and lipid metabolic pathways, leading to high cholesterol levels in T-IEL; suppression of T cell antigen receptor signalling and expression of the transcription factor TOX, reminiscent of chronically activated T cells. These novel findings illustrate how T-IEL integrate multiple tissue-specific signals to maintain their homeostasis and potentially function.
Keywords: T lymphocytes; immunology; immunometabolism; inflammation; intestinal immunity; mouse; proteomics.
© 2021, Brenes et al.
Conflict of interest statement
AB, OJ, HW, JH, LS, DD, AL, MS None, MV none
Figures



References
-
- Alfei F, Kanev K, Hofmann M, Wu M, Ghoneim HE, Roelli P, Utzschneider DT, von Hoesslin M, Cullen JG, Fan Y, Eisenberg V, Wohlleber D, Steiger K, Merkler D, Delorenzi M, Knolle PA, Cohen CJ, Thimme R, Youngblood B, Zehn D. TOX reinforces the phenotype and longevity of exhausted T cells in chronic viral infection. Nature. 2019;571:265–269. doi: 10.1038/s41586-019-1326-9. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Allan C, Burel J-M, Moore J, Blackburn C, Linkert M, Loynton S, Macdonald D, Moore WJ, Neves C, Patterson A, Porter M, Tarkowska A, Loranger B, Avondo J, Lagerstedt I, Lianas L, Leo S, Hands K, Hay RT, Patwardhan A, Best C, Kleywegt GJ, Zanetti G, Swedlow JR. OMERO: Flexible, model-driven data management for experimental biology. Nature Methods. 2012;9:245–253. doi: 10.1038/nmeth.1896. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Argüello RJ, Combes AJ, Char R, Gigan JP, Baaziz AI, Bousiquot E, Camosseto V, Samad B, Tsui J, Yan P, Boissonneau S, Figarella-Branger D, Gatti E, Tabouret E, Krummel MF, Pierre P. SCENITH: A Flow Cytometry-Based Method to Functionally Profile Energy Metabolism with Single-Cell Resolution. Cell Metabolism. 2020;32:1063–1075. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2020.11.007. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Borges da Silva H, Beura LK, Wang H, Hanse EA, Gore R, Scott MC, Walsh DA, Block KE, Fonseca R, Yan Y, Hippen KL, Blazar BR, Masopust D, Kelekar A, Vulchanova L, Hogquist KA, Jameson SC. The purinergic receptor P2RX7 directs metabolic fitness of long-lived memory CD8+ T cells. Nature. 2018;559:264–268. doi: 10.1038/s41586-018-0282-0. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

