Association Between COVID-19 and Myocarditis Using Hospital-Based Administrative Data - United States, March 2020-January 2021
- PMID: 34473684
- PMCID: PMC8422872
- DOI: 10.15585/mmwr.mm7035e5
Association Between COVID-19 and Myocarditis Using Hospital-Based Administrative Data - United States, March 2020-January 2021
Abstract
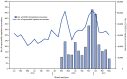
Viral infections are a common cause of myocarditis, an inflammation of the heart muscle (myocardium) that can result in hospitalization, heart failure, and sudden death (1). Emerging data suggest an association between COVID-19 and myocarditis (2-5). CDC assessed this association using a large, U.S. hospital-based administrative database of health care encounters from >900 hospitals. Myocarditis inpatient encounters were 42.3% higher in 2020 than in 2019. During March 2020-January 2021, the period that coincided with the COVID-19 pandemic, the risk for myocarditis was 0.146% among patients diagnosed with COVID-19 during an inpatient or hospital-based outpatient encounter and 0.009% among patients who were not diagnosed with COVID-19. After adjusting for patient and hospital characteristics, patients with COVID-19 during March 2020-January 2021 had, on average, 15.7 times the risk for myocarditis compared with those without COVID-19 (95% confidence interval [CI] = 14.1-17.2); by age, risk ratios ranged from approximately 7.0 for patients aged 16-39 years to >30.0 for patients aged <16 years or ≥75 years. Overall, myocarditis was uncommon among persons with and without COVID-19; however, COVID-19 was significantly associated with an increased risk for myocarditis, with risk varying by age group. These findings underscore the importance of implementing evidence-based COVID-19 prevention strategies, including vaccination, to reduce the public health impact of COVID-19 and its associated complications.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have completed and submitted the International Committee of Medical Journal Editors form for disclosure of potential conflicts of interest. No potential conflicts of interest were disclosed.
Figures

References
-
- Rathore SS, Rojas GA, Sondhi M, et al. Myocarditis associated with Covid-19 disease: a systematic review of published case reports and case series. Int J Clin Pract 2021;e14470. Epub July 7, 2021. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

