Rats use memory confidence to guide decisions
- PMID: 34473948
- PMCID: PMC8551068
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cub.2021.08.013
Rats use memory confidence to guide decisions
Abstract
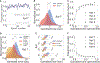
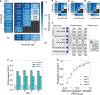
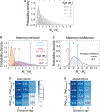
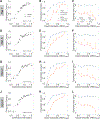
Memory enables access to past experiences to guide future behavior. Humans can determine which memories to trust (high confidence) and which to doubt (low confidence). How memory retrieval, memory confidence, and memory-guided decisions are related, however, is not understood. In particular, how confidence in memories is used in decision making is unknown. We developed a spatial memory task in which rats were incentivized to gamble their time: betting more following a correct choice yielded greater reward. Rat behavior reflected memory confidence, with higher temporal bets following correct choices. We applied machine learning to identify a memory decision variable and built a generative model of memories evolving over time that accurately predicted both choices and confidence reports. Our results reveal in rats an ability thought to exist exclusively in primates and introduce a unified model of memory dynamics, retrieval, choice, and confidence.
Keywords: behavior; confidence; decision making; deep neural network; machine learning; memory; metamemory; rat; spatial memory.
Copyright © 2021 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Comment in
-
Metamemory: Rats know the strength of their memory.Curr Biol. 2021 Nov 8;31(21):R1432-R1434. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2021.09.062. Curr Biol. 2021. PMID: 34752769 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Memory states influence value-based decisions.J Exp Psychol Gen. 2016 Nov;145(11):1420-1426. doi: 10.1037/xge0000231. J Exp Psychol Gen. 2016. PMID: 27797556 Free PMC article.
-
Sensorimotor learning biases choice behavior: a learning neural field model for decision making.PLoS Comput Biol. 2012;8(11):e1002774. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1002774. Epub 2012 Nov 15. PLoS Comput Biol. 2012. PMID: 23166483 Free PMC article.
-
Reinstated episodic context guides sampling-based decisions for reward.Nat Neurosci. 2017 Jul;20(7):997-1003. doi: 10.1038/nn.4573. Epub 2017 Jun 5. Nat Neurosci. 2017. PMID: 28581478
-
Hippocampal-cortical interaction in decision making.Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2015 Jan;117:34-41. doi: 10.1016/j.nlm.2014.02.002. Epub 2014 Feb 13. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 2015. PMID: 24530374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reward-dependent learning in neuronal networks for planning and decision making.Prog Brain Res. 2000;126:217-29. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(00)26016-0. Prog Brain Res. 2000. PMID: 11105649 Review.
Cited by
-
Stimulus uncertainty and relative reward rates determine adaptive responding in perceptual decision-making.PLoS Comput Biol. 2025 May 27;21(5):e1012636. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012636. eCollection 2025 May. PLoS Comput Biol. 2025. PMID: 40424292 Free PMC article.
-
Parahippocampal neurons encode task-relevant information for goal-directed navigation.Elife. 2024 Feb 16;12:RP85646. doi: 10.7554/eLife.85646. Elife. 2024. PMID: 38363198 Free PMC article.
-
Natural statistics support a rational account of confidence biases.Nat Commun. 2023 Jul 6;14(1):3992. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-39737-2. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37414780 Free PMC article.
-
A cognitive process model captures near-optimal confidence-guided waiting in rats.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jun 20:2024.06.07.597954. doi: 10.1101/2024.06.07.597954. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38895394 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Metamemory: Rats know the strength of their memory.Curr Biol. 2021 Nov 8;31(21):R1432-R1434. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2021.09.062. Curr Biol. 2021. PMID: 34752769 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

