Large-scale cis- and trans-eQTL analyses identify thousands of genetic loci and polygenic scores that regulate blood gene expression
- PMID: 34475573
- PMCID: PMC8432599
- DOI: 10.1038/s41588-021-00913-z
Large-scale cis- and trans-eQTL analyses identify thousands of genetic loci and polygenic scores that regulate blood gene expression
Abstract
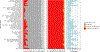
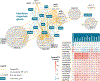
Trait-associated genetic variants affect complex phenotypes primarily via regulatory mechanisms on the transcriptome. To investigate the genetics of gene expression, we performed cis- and trans-expression quantitative trait locus (eQTL) analyses using blood-derived expression from 31,684 individuals through the eQTLGen Consortium. We detected cis-eQTL for 88% of genes, and these were replicable in numerous tissues. Distal trans-eQTL (detected for 37% of 10,317 trait-associated variants tested) showed lower replication rates, partially due to low replication power and confounding by cell type composition. However, replication analyses in single-cell RNA-seq data prioritized intracellular trans-eQTL. Trans-eQTL exerted their effects via several mechanisms, primarily through regulation by transcription factors. Expression of 13% of the genes correlated with polygenic scores for 1,263 phenotypes, pinpointing potential drivers for those traits. In summary, this work represents a large eQTL resource, and its results serve as a starting point for in-depth interpretation of complex phenotypes.
© 2021. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature America, Inc.
Figures





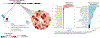

References
References for main text
-
- Zeng J et al. Signatures of negative selection in the genetic architecture of human complex traits. Nature Genetics 50, 746–753 (2018). - PubMed
Methods-only references
-
- Westra HJ et al. MixupMapper: Correcting sample mix-ups in genome-wide datasets increases power to detect small genetic effects. Bioinformatics 27, 2104–2111 (2011). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- MC_PC_19009/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HG008150/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH109905/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AG073104/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES023834/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL105756/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES020506/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_15018/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- 201488/Z/16/Z/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 CA107431/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 ES024834/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R35 ES028379/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH101814/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- G9815508/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 GM108711/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

