Nasal Administration of Anti-CD3 Monoclonal Antibody (Foralumab) Reduces Lung Inflammation and Blood Inflammatory Biomarkers in Mild to Moderate COVID-19 Patients: A Pilot Study
- PMID: 34475873
- PMCID: PMC8406802
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.709861
Nasal Administration of Anti-CD3 Monoclonal Antibody (Foralumab) Reduces Lung Inflammation and Blood Inflammatory Biomarkers in Mild to Moderate COVID-19 Patients: A Pilot Study
Erratum in
-
Corrigendum: Nasal Administration of Anti-CD3 Monoclonal Antibody (Foralumab) Reduces Lung Inflammation and Blood Inflammatory Biomarkers in Mild to Moderate COVID-19 Patients: A Pilot Study.Front Immunol. 2022 Jan 12;12:815812. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.815812. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35095916 Free PMC article.
Abstract
Background: Immune hyperactivity is an important contributing factor to the morbidity and mortality of COVID-19 infection. Nasal administration of anti-CD3 monoclonal antibody downregulates hyperactive immune responses in animal models of autoimmunity through its immunomodulatory properties. We performed a randomized pilot study of fully-human nasal anti-CD3 (Foralumab) in patients with mild to moderate COVID-19 to determine if its immunomodulatory properties had ameliorating effects on disease.
Methods: Thirty-nine outpatients with mild to moderate COVID-19 were recruited at Santa Casa de Misericordia de Santos in Sao Paulo State, Brazil. Patients were randomized to three cohorts: 1) Control, no Foralumab (n=16); 2) Nasal Foralumab (100ug/day) given for 10 consecutive days with 6 mg dexamethasone given on days 1-3 (n=11); and 3) Nasal Foralumab alone (100ug/day) given for 10 consecutive days (n=12). Patients continued standard of care medication.
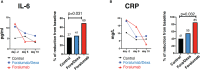
Results: We observed reduction of serum IL-6 and C-reactive protein in Foralumab alone vs. untreated or Foralumab/Dexa treated patients. More rapid clearance of lung infiltrates as measured by chest CT was observed in Foralumab and Foralumab/Dexa treated subjects vs. those that did not receive Foralumab. Foralumab treatment was well-tolerated with no severe adverse events.
Conclusions: This pilot study suggests that nasal Foralumab is well tolerated and may be of benefit in treatment of immune hyperactivity and lung involvement in COVID-19 disease and that further studies are warranted.
Keywords: COVID-19; SARS-CoV-2; anti-CD3; foralumab; immune responses.
Copyright © 2021 Moreira, Matos, De Paula, Santana, Da Mata, Pansera, Cortina, Spinola, Keppeke, Jacob, Palejwala, Chen, Izzy, Healey, Rezende, Dedivitis, Shailubhai and Weiner.
Conflict of interest statement
JJ, VP and KS are employees of Tiziana, Life Sciences. HW is chair of the Scientific Advisory Board of Tiziana and received consulting fees and stock options from the company. TM and KM received consulting fees from the company. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

