MicroRNA‑502‑3p promotes Mycobacterium tuberculosis survival in macrophages by modulating the inflammatory response by targeting ROCK1
- PMID: 34476503
- PMCID: PMC8436224
- DOI: 10.3892/mmr.2021.12393
MicroRNA‑502‑3p promotes Mycobacterium tuberculosis survival in macrophages by modulating the inflammatory response by targeting ROCK1
Abstract
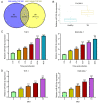
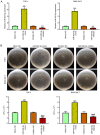
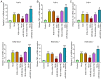
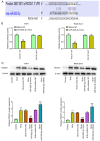
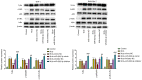
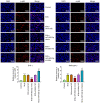
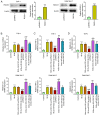
Tuberculosis (TB) is caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis) infection and has the highest mortality rate of any single infectious disease worldwide. The aim of the present study was to investigate the function of microRNA (miR)‑502‑3p in M. tuberculosis‑infected macrophages. The Gene Expression Omnibus database was used to analyze miR‑502‑3p expression in patients with TB and healthy individuals. THP‑1 and RAW 264.7 cells were transfected with miR‑502‑3p mimic, miR‑502‑3p inhibitor, pcDNA3.1‑ROCK1 or their negative controls. The expression levels of miR‑502‑3p and inflammatory cytokines were evaluated using reverse transcription‑quantitative PCR. The colony‑forming unit assay was performed to assess the survival of M. tuberculosis in macrophages, and Toll‑like receptor (TLR)4/NF‑κB signaling pathway‑associated protein expression levels were detected by western blotting. The nuclear translocation of NF‑κB p65 was detected via immunocytochemistry. TargetScan was used to predict the binding sites between miR‑502‑3p and ROCK1. The interaction between miR‑502‑3p and Rho‑associated coiled‑coil‑forming protein kinase 1 (ROCK1) was confirmed using a dual‑luciferase reporter assay; ROCK1 was demonstrated to be a direct target gene of miR‑502‑3p. Results from the present study demonstrated that miR‑502‑3p expression was significantly increased during M. tuberculosis infection in macrophages. Upregulation of miR‑502‑3p expression levels significantly enhanced the survival of intracellular M. tuberculosis. IL‑6, TNF‑α, and IL‑1β mRNA expression levels were significantly upregulated during M. tuberculosis infection but were downregulated by miR‑502‑3p overexpression. Moreover, miR‑502‑3p mimics transfection significantly downregulated TLR4/NF‑κB signaling pathway‑associated protein expression and significantly reduced nuclear transcription of NF‑κB in M. tuberculosis‑infected macrophages. ROCK1 overexpression reversed the miR‑502‑3p inhibitory effect on cytokine production in M. tuberculosis‑infected macrophages. In conclusion, miR‑502‑3p/ROCK1 may serve an anti‑inflammatory role and may improve the survival of M. tuberculosis within macrophages, which may provide a promising therapeutic target for TB.
Keywords: Mycobacterium tuberculosis; Rho‑associated coiled-coil-forming protein kinase 1; inflammation; macrophages; microRNA‑502‑3p.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-708-5p regulates mycobacterial vitality and the secretion of inflammatory factors in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected macrophages by targeting TLR4.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019 Sep;23(18):8028-8038. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_201909_19019. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019. PMID: 31599428
-
MicroRNA-20a-3p regulates the host immune response to facilitate the mycobacterium tuberculosis infection by targeting IKKβ/NF-κB pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2021 Feb;91:107286. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2020.107286. Epub 2020 Dec 29. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021. PMID: 33385712
-
MiR-1178 regulates mycobacterial survival and inflammatory responses in Mycobacterium tuberculosis-infected macrophages partly via TLR4.J Cell Biochem. 2018 Sep;119(9):7449-7457. doi: 10.1002/jcb.27054. Epub 2018 May 21. J Cell Biochem. 2018. PMID: 29781535
-
MicroRNAs play big roles in modulating macrophages response toward mycobacteria infection.Infect Genet Evol. 2016 Nov;45:378-382. doi: 10.1016/j.meegid.2016.09.023. Epub 2016 Sep 28. Infect Genet Evol. 2016. PMID: 27693402 Review.
-
Combating Tuberculosis via Restoring the Host Immune Capacity by Targeting M. tb Kinases and Phosphatases.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 20;25(22):12481. doi: 10.3390/ijms252212481. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39596546 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Role of MicroRNA-502-3p in Human Diseases.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Apr 2;16(4):532. doi: 10.3390/ph16040532. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37111289 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune regulation and emerging roles of noncoding RNAs in Mycobacterium tuberculosis infection.Front Immunol. 2022 Oct 13;13:987018. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.987018. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36311754 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Efficacy of ripasudil in reducing intraocular pressure and medication score for ocular hypertension with inflammation and corticosteroid.Int J Ophthalmol. 2023 Jun 18;16(6):904-908. doi: 10.18240/ijo.2023.06.11. eCollection 2023. Int J Ophthalmol. 2023. PMID: 37332549 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alzahabi KH, Usmani O, Georgiou TK, Ryan MP, Robertson BD, Tetley TD, Porter AE. Approaches to treating tuberculosis by encapsulating metal ions and anti-mycobacterial drugs utilizing nano- and microparticle technologies. Emerg Top Life Sci. 2020;4:581–600. doi: 10.1042/ETLS20190154. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

