Sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor, Empagliflozin, is associated with significant reduction in weight, body mass index, fasting glucose, and A1c levels in Type 2 diabetic patients with established coronary heart disease: the SUPER GATE study
- PMID: 34476725
- PMCID: PMC8412859
- DOI: 10.1007/s11845-021-02761-6
Sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitor, Empagliflozin, is associated with significant reduction in weight, body mass index, fasting glucose, and A1c levels in Type 2 diabetic patients with established coronary heart disease: the SUPER GATE study
Abstract
Background: Empagliflozin, a sodium-glucose co-transporter-2 (SGLT-2) inhibitor, yielded significant beneficiaries in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). It is particularly benefited the diabetic subjects with heart conditions.
Aims: We aimed to obtain a real-world data about the effects of empagliflozin add-on treatment on metabolic parameters, cardiovascular risk factors, and anthropometric measures in patients with T2DM.
Methods: Type 2 diabetic patients with established coronary heart disease whom empagliflozin added to their treatment were enrolled in the study. Anthropometric measures, clinical and laboratory data, were obtained before and at the 6th month of the empagliflozin treatment. All data before and at the 6th month were compared.
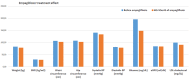
Results: Body weight (p < 0.001), body mass index (p < 0.001), waist (p < 0.001) and hip (p < 0.001) circumferences, systolic blood pressure (p = 0.006), heart rate (p = 0.01), LDL cholesterol (p = 0.01), fasting plasma glucose (p < 0.001), and HbA1c (p < 0.001) levels were significantly reduced on 6th month of empagliflozin treatment compared to the baseline values. Estimated GFR (p = 0.66), serum creatinine (p = 0.8), uric acid (p = 0.40), total cholesterol (p = 0.053), triglyceride (p = 0.057), and HDL (p = 0.09) levels were not significantly changed.
Conclusions: We suggest that empagliflozin treatment may improve anthropometric measures, metabolic parameters, and blood pressure and does not cause deterioration in kidney functions in type 2 diabetic patients with established coronary heart disease.
Keywords: Coronary heart disease; Empagliflozin; Fasting glucose; HbA1c; Type 2 diabetes mellitus.
© 2021. Royal Academy of Medicine in Ireland.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Chen MB, Wang H, Zheng QH, Xu HL, Cui WY. Effect of sodium-dependent glucose transporter inhibitors on glycated hemoglobin A1c after 24 weeks in patients with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2021;100(1):e24101. doi: 10.1097/md.0000000000024101. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Nassif ME, Qintar M, Windsor SL, Jermyn R, Shavelle DM, Tang F, Lamba S, Bhatt K, Brush J, Civitello A, Gordon R, Jonsson O, Lampert B, Pelzel J, Kosiborod MN. Empagliflozin effects on pulmonary artery pressure in patients with heart failure: results from the EMBRACE-HF Trial. Circulation. 2021;143(17):1673–1686. doi: 10.1161/circulationaha.120.052503. - DOI - PubMed
-
- von Lewinski D, Benedikt M, Tripolt N, Wallner M, Sourij H, Kolesnik E. Can sodium glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT-2) inhibitors be beneficial in patients with acute myocardial infarction? Kardiol Pol. 2021;79(5):503–509. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical