A novel rat model of vertebral inflammation-induced intervertebral disc degeneration mediated by activating cGAS/STING molecular pathway
- PMID: 34477314
- PMCID: PMC8505843
- DOI: 10.1111/jcmm.16898
A novel rat model of vertebral inflammation-induced intervertebral disc degeneration mediated by activating cGAS/STING molecular pathway
Abstract
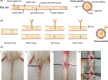
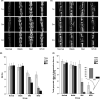
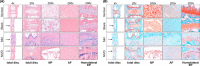
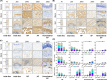
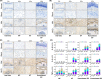
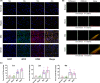
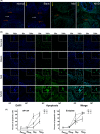
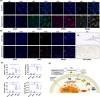
In this study, we describe a new rat model of vertebral inflammation-induced caudal intervertebral disc degeneration (VI-IVDD), in which IVD structure was not damaged and controllable segment and speed degeneration was achieved. VI-IVDD model was obtained by placing lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in the caudal vertebral bodies of rats. Rat experimental groups were set as follows: normal control group, group with a hole drilled in the middle of vertebral body and not filled with LPS (Blank group), group with a hole drilled in the middle of vertebral body and filled with LPS (Mid group), and group with hole drilled in the vertebral body in proximity of IVD and filled with LPS (NIVD group). Radiological results of VI-IVDD rats showed a significant reduction in the intervertebral space height and decrease in MRI T2 signal intensity. Histological stainings also revealed that the more the nucleus pulposus and endplate degenerated, the more the annulus fibrosus structure appeared disorganized. Immunohistochemistry analysis demonstrated that the expression of Aggrecan and collagen-II decreased, whereas that of MMP-3 increased in Mid and NIVD groups. Abundant local production of pro-inflammatory cytokines was detected together with increased infiltration of M1 macrophages in Mid and NIVD groups. Apoptosis ratio remarkably enhanced in Mid and NIVD groups. Interestingly, we found a strong activation of the cyclic GMP-AMP synthase /stimulator of interferon gene signalling pathway, which is strictly related to inflammatory and degenerative diseases. In this study, we generated a new, reliable and reproducible IVDD rat model, in which controllable segment and speed degeneration was achieved.
Keywords: animal model; cGAS/STING signalling pathway; intervertebral disc degeneration; spread of inflammation; vertebral inflammation-induced intervertebral disc degeneration model.
© 2021 The Authors. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine published by Foundation for Cellular and Molecular Medicine and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship and/or publication of this article.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Targeting STING attenuates ROS induced intervertebral disc degeneration.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021 Aug;29(8):1213-1224. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2021.04.017. Epub 2021 May 19. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2021. PMID: 34020031
-
EZH2 inhibits senescence-associated inflammation and attenuates intervertebral disc degeneration by regulating the cGAS/STING pathway via H3K27me3.Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2025 May;33(5):548-559. doi: 10.1016/j.joca.2025.02.771. Epub 2025 Feb 10. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2025. PMID: 39938633
-
CB2-mediated attenuation of nucleus pulposus degeneration via the amelioration of inflammation and oxidative stress in vivo and in vitro.Mol Med. 2021 Aug 19;27(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s10020-021-00351-x. Mol Med. 2021. PMID: 34412587 Free PMC article.
-
Progress in understanding the role of cGAS-STING pathway associated with programmed cell death in intervertebral disc degeneration.Cell Death Discov. 2023 Oct 16;9(1):377. doi: 10.1038/s41420-023-01607-7. Cell Death Discov. 2023. PMID: 37845198 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of the Wnt pathway in the formation, development, and degeneration of intervertebral discs.Pathol Res Pract. 2021 Apr;220:153366. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2021.153366. Epub 2021 Feb 8. Pathol Res Pract. 2021. PMID: 33647863 Review.
Cited by
-
Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells Inhibit Oxidative Stress-Induced Pyroptosis in Annulus Fibrosus Cells to Alleviate Intervertebral Disc Degeneration Based on Matric Hydrogels.Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024 Nov;196(11):8043-8057. doi: 10.1007/s12010-024-04953-z. Epub 2024 Apr 27. Appl Biochem Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38676833
-
The regulatory mechanism of cyclic GMP-AMP synthase on inflammatory senescence of nucleus pulposus cell.J Orthop Surg Res. 2024 Jul 22;19(1):421. doi: 10.1186/s13018-024-04919-1. J Orthop Surg Res. 2024. PMID: 39034400 Free PMC article.
-
Histological characteristics of exercise-induced skeletal muscle remodelling.J Cell Mol Med. 2023 Nov;27(21):3217-3234. doi: 10.1111/jcmm.17879. Epub 2023 Jul 30. J Cell Mol Med. 2023. PMID: 37517049 Free PMC article.
-
Pyroptosis and Intervertebral Disc Degeneration: Mechanistic Insights and Therapeutic Implications.J Inflamm Res. 2022 Oct 17;15:5857-5871. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S382069. eCollection 2022. J Inflamm Res. 2022. PMID: 36263145 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting STING: From antiviral immunity to treat osteoporosis.Front Immunol. 2023 Jan 18;13:1095577. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1095577. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 36741390 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

