An isotropic EPI database and analytical pipelines for rat brain resting-state fMRI
- PMID: 34478824
- PMCID: PMC8561231
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2021.118541
An isotropic EPI database and analytical pipelines for rat brain resting-state fMRI
Abstract
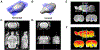
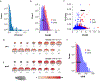
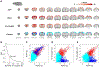
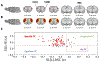
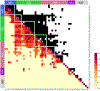
Resting-state functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) has drastically expanded the scope of brain research by advancing our knowledge about the topologies, dynamics, and interspecies translatability of functional brain networks. Several databases have been developed and shared in accordance with recent key initiatives in the rodent fMRI community to enhance the transparency, reproducibility, and interpretability of data acquired at various sites. Despite these pioneering efforts, one notable challenge preventing efficient standardization in the field is the customary choice of anisotropic echo planar imaging (EPI) schemes with limited spatial coverage. Imaging with anisotropic resolution and/or reduced brain coverage has significant shortcomings including reduced registration accuracy and increased deviation in brain feature detection. Here we proposed a high-spatial-resolution (0.4 mm), isotropic, whole-brain EPI protocol for the rat brain using a horizontal slicing scheme that can maintain a functionally relevant repetition time (TR), avoid high gradient duty cycles, and offer unequivocal whole-brain coverage. Using this protocol, we acquired resting-state EPI fMRI data from 87 healthy rats under the widely used dexmedetomidine sedation supplemented with low-dose isoflurane on a 9.4 T MRI system. We developed an EPI template that closely approximates the Paxinos and Watson's rat brain coordinate system and demonstrated its ability to improve the accuracy of group-level approaches and streamline fMRI data pre-processing. Using this database, we employed a multi-scale dictionary-learning approach to identify reliable spatiotemporal features representing rat brain intrinsic activity. Subsequently, we performed k-means clustering on those features to obtain spatially discrete, functional regions of interest (ROIs). Using Euclidean-based hierarchical clustering and modularity-based partitioning, we identified the topological organizations of the rat brain. Additionally, the identified group-level FC network appeared robust across strains and sexes. The "triple-network" commonly adapted in human fMRI were resembled in the rat brain. Through this work, we disseminate raw and pre-processed isotropic EPI data, a rat brain EPI template, as well as identified functional ROIs and networks in standardized rat brain coordinates. We also make our analytical pipelines and scripts publicly available, with the hope of facilitating rat brain resting-state fMRI study standardization.
Keywords: Database; Echo planar imaging; Functional connectivity; Rat; Resting state fMRI.
Copyright © 2021. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures



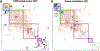

References
-
- Adhikari BM, Jahanshad N, Shukla D, Turner J, Grotegerd D, Dannlowski U, Kugel H, Engelen J, Dietsche B, Krug A, Kircher T, Fieremans E, Veraart J, Novikov DS, Boedhoe PSW, van der Werf YD, van den Heuvel OA, Ipser J, Uhlmann A, Stein DJ, Dickie E, Voineskos AN, Malhotra AK, Pizzagalli F, Calhoun VD, Waller L, Veer IM, Walter H, Buchanan RW, Glahn DC, Hong LE, Thompson PM, Kochunov P, 2019. A resting state fMRI analysis pipeline for pooling inference across diverse cohorts: an ENIGMA rs-fMRI protocol. Brain Imaging Behav. 13, 1453–1467. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Alfaro-Almagro F, Jenkinson M, Bangerter NK, Andersson JLR, Griffanti L, Douaud G, Sotiropoulos SN, Jbabdi S, Hernandez-Fernandez M, Vallee E, Vidaurre D, Webster M, McCarthy P, Rorden C, Daducci A, Alexander DC, Zhang H, Dragonu I, Matthews PM, Miller KL, Smith SM, 2018. Image processing and Quality Control for the first 10,000 brain imaging datasets from UK Biobank. Neuroimage 166, 400–424. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P50 HD103573/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 MH117053/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- R25 GM055336/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R44 NS105500/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH126518/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- K01 AA025383/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- U01 AA020023/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 MH111429/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- S10 OD026796/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- P60 AA011605/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS091236/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R41 MH113252/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- U24 AA020024/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AA025582/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- R43 DA051265/DA/NIDA NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

